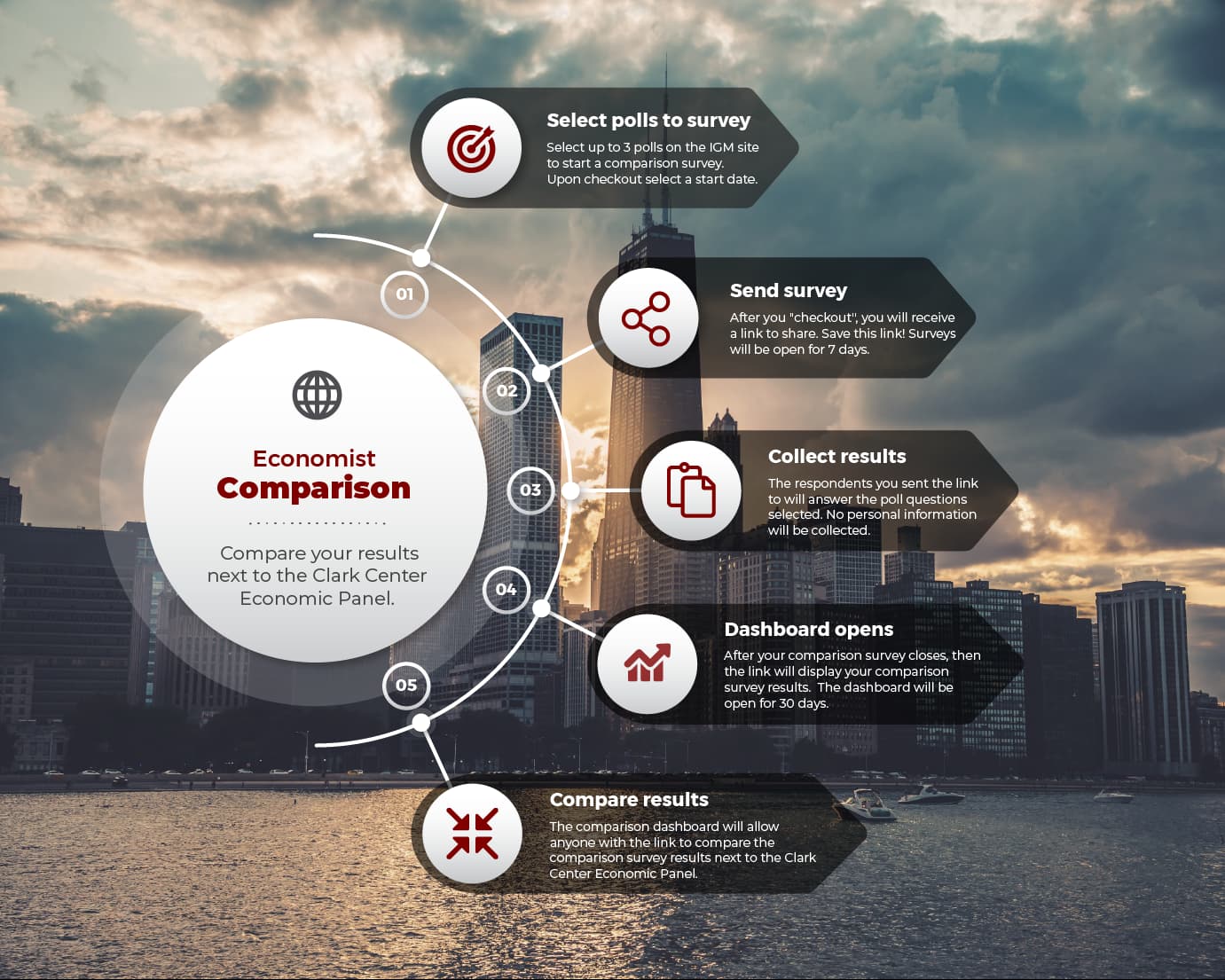
About
- Arthur Williams Phillips Professor of Economics
- 2016 Bernacer prize
- Director of ESRC Centre for Macroeconomics (UK)
Voting History
Question A: The reductions in Western programs of development assistance will have no measurable effects on GDP growth in the recipient countries over the next five years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
6 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
Comment: The association between aid and GDP growth is weak in the data,
-see background information here |
|||
Question B: The reductions in Western programs of development assistance will have substantially negative effects on the most vulnerable people in the recipient countries over the next five years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: Especially in disaster relief, but not only. There can be large welfare gains in providing social insurance, beyond GDP effects.
-see background information here |
|||
Question C: Development assistance motivated by the potential benefits for the donors in terms of prosperity and security is measurably more effective in promoting GDP growth in recipient countries than aid based on humanitarian or other moral principles.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
8 |
Disagree |
5 |
|
Comment: Aid-growth literature would suggest the opposite
|
|||
Question A: Matching US import tariffs to the tariffs, value-added taxes and non-tariff barriers imposed on US goods by other countries would substantially reduce the US trade deficit.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: The threat of retaliation against the imposition of higher tariffs on a country’s exports substantially lowers the probability of a trade war.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C: In the event that the threat of retaliation does not deter the imposition of tariffs, the economies of countries subject to higher tariffs on their exports would be measurably better off by responding with targeted tariffs on imports from the first mover.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: The wave of immigration to Germany after 2015 (and up to the Russian invasion of Ukraine) has been a net positive for the country's economy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
7 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Immigration to EU countries has been a net positive for government finances, adding substantially more in tax revenues than the increased costs associated with integration of immigrants.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
7 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: Not "substantially" more, taking a present value intertemporal perspective.
|
|||
Question C: Given Europe's low and falling fertility rates (from seven million births per year in 1960 to four million today), maintaining its position as a world economic power will require increased immigration over the medium term.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
7 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: (i) no clear empirical relation between the size of population and economic growth (scale effects) (ii) Europe is currently quite high population density, (iii) the decline in fertility is not inevitable, and can change.
|
|||
Question A: Putting America First in International Environmental Agreements: https://www.whitehouse.gov/presidential-actions/2025/01/putting-america-first-in-international-environmental-agreements/
'In recent years, the United States has purported to join international agreements and initiatives that do not reflect our country's values or our contributions to the pursuit of economic and environmental objectives... The United States Ambassador to the United Nations shall immediately submit formal written notification of the United States' withdrawal from the Paris Agreement under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change.'
US withdrawal from the Paris climate agreement will deliver a measurable boost to the country's economic growth over the next four years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
6 |
Disagree |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question B: US withdrawal from the Paris climate agreement will have a measurably negative impact on international progress on mitigation of global warming.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A: A baseline US tariff of 10% on all European imported goods would have substantially damaging economic consequences for many countries in Europe.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
6 |
Question B: Rather than responding to threatened tariffs with retaliatory measures, unilaterally opening EU markets to US exports would deliver better outcomes for European industry.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
3 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: Depends on industry by industry, overall maybe yes.
|
|||
Question C: Disruptions to global supply chains from new tariffs and trade wars will lead to measurably slower global growth over the next five years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Agree |
6 |
Question A: The likely need for increased European public investment in defense should come with substantial reallocations of public budgets at the national and EU levels.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: There is a budget constraint.
|
|||
Question B: Greater use of joint EU-level procurement of military equipment and defense research/innovation would promote substantially enhanced capacity in Europe's defense industry.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
5 |
Agree |
5 |
|
Comment: By itself, demand does not create its own supply in an economy open to trade.
|
|||
Question C: Increased defense spending would deliver a measurable boost to economic growth in Europe over the next five years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
6 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: It depends on what that defense spending is on. If, for instance (but sadly not hypothetically), if defense spending means spending on pensions of retired personal, then no.
|
|||
On the basis of current climate policy commitments and potential technology and market responses, my current best estimate for global warming is that average global temperatures by 2100 will rise to no more than 2.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
3 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: From IPCC latest report:"The best estimates [and very likely ranges] for the different scenarios are: 1.4 [1.0 to 1.8 ]°C (SSP1-1.9); 1.8 [1.3 to 2.4]°C (SSP1-2.6); 2.7 [2.1 to 3.5]°C (SSP2-4.5); 3.6 [2.8 to 4.6]°C (SSP3-7.0); and 4.4 [3.3 to 5.7 ]°C (SSP5-8.5)." Very uncertain.
-see background information here |
|||
Question A: A period of high inflation is substantially more electorally damaging to incumbent governments in advanced countries than a period of high unemployment.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
7 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: It depends on what is "high" on both. But, the last three years of US data teaches us little about this, since there was almost no increase in unemployment. If inflation had peaked at 6% but unemployment had risen above 6%, wouldn't Harris have lost by even more?
-see background information here |
|||
Question B: Voters are more likely to punish incumbents for what they perceive as poor national economic performance than they are to reward incumbents for a good economy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
6 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: Loss aversion and reference dependence would suggest this, but I do not know of direct evidence for it in the election/macroeconomy context
-see background information here |
|||
Question A: The institutions of society - such as constitutions, laws, judiciaries, and property rights - substantially shape economic decisions, policies, and outcomes.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
7 |
Strongly Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question B: On average and over the long term, democracies deliver substantially better economic growth than other forms of government.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
3 |
Agree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question C: Countries where democracy and the rule of law are weakened are likely to experience measurable damage to their economic performance.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
4 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Current enforcement of competition policy in Europe is not working to promote innovation and growth.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
7 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question B: European Union bureaucracy and regulations are a substantial constraint on innovation in Europe.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
7 |
Agree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question C: The conduct of the dominant US tech companies in European markets (including lobbying and acquisition of start-ups and competitors) is a substantial constraint on innovation in Europe.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
4 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question A: In pursuing social and environmental initiatives, the average public company generates more benefits than costs in terms of profits.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
7 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: Unless the initiatives are perfectly aligned with profits (unlikely) there will be trade-offs. I worry more that these initiatives are loosely defined so they end up giving free rein for managers to pursue own interests, hurt governance, and enhance principal-agent problems.
|
|||
Question B: In pursuing social and environmental initiatives, public companies would benefit from a measurably lower cost of capital.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
6 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: It can in theory (see link), and some papers have found that it has been the case in the recent past, partly because of mandates imposed by institutional investors.
-see background information here |
|||
Question C: There are substantial social benefits when managers of public companies make choices that account for the impact of their decisions on customers, employees, and community members beyond the effects on shareholders.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
6 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: Substantial is too strong, especially given my concerns about principal-agent problems and corporate governance in first question.
|
|||
Question A: US antitrust investigations of the dominant firms in artificial intelligence are warranted by the need to foster competition and innovation in the technologies.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
6 |
Agree |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Seeking to slow the pace of artificial intelligence use and implementation would be a more effective means of assessing potential harms from the technologies than market deployment and ex post assessment.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
7 |
Uncertain |
4 |
|
|
|||
Question A: The proposed US tariffs on Chinese EVs would lead to measurably higher employment in the US automotive industry over the next five years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
6 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: Only in the short run, and that may be a quite short time.
|
|||
Question B: The proposed US tariffs on Chinese EVs would measurably slow the adoption of green technology by consumers.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
8 |
Agree |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question C: Unless the EU matches the proposed US tariffs on Chinese EVs, there would be measurably lower employment in Europe's automotive industry over the next five years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
3 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Greater integration of national markets for financial services, energy and telecommunications would give a measurable boost to Europe’s GDP over the next ten years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
4 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: European companies seem to suffer from an under-scaling disadvantage in today's digital economy.
|
|||
Question B: The potential benefits for GDP from loosening European merger rules to allow greater consolidation within the single market would outweigh the potential harm to consumers from weaker competition.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Disagree |
7 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: Weaker competition is, too often, much weaker competition. This is the new mercantilism in that, again, it comes from focussing on producer surplus and neglecting consumer surplus.
|
|||
Question A:Creation of a more unified capital market in Europe - with a common pool of capital, a single rule book and a strengthened European Securities and Markets Authority, comparable to the US Securities and Exchange Commission – would lead to a substantial shift in the balance of companies listing their shares in the EU vis-a-vis the US.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
6 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: Not enough, however.
|
|||
Question B: Creation of a more unified capital market in Europe - with a common pool of capital, a single rule book and a strengthened European Securities and Markets Authority, comparable to the US Securities and Exchange Commission – would substantially increase the availability of funding for start-ups and growing companies across the EU.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
6 |
Agree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question A: The European Union's AI Act was approved by the European Parliament in March 2024: https://artificialintelligenceact.eu/the-act/
The EU's legislation to regulate artificial intelligence is likely to put European technology firms at a substantial disadvantage to their competitors elsewhere in the world.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: By providing a clear set of rules, the EU's legislation on artificial intelligence is likely to enhance research and innovation by firms building the new technology.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
4 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Europe’s economic growth performance over the last 25 years has been measurably better than it would have been in the absence of the single currency.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
4 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: Since the performance was mediocre, one may dream of a rosier alternative. But, insofar as we would have the two big shocks---a financial crisis in 2007-08 and a pandemic in 2020 anyway---without the euro, many EA regions would have done much worse in response to them.
|
|||
Question B: With euro area member states having given up their ability to carry out independent monetary policy, it is substantially more difficult for them to respond effectively to country-specific macroeconomic disturbances.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
7 |
Uncertain |
8 |
|
Comment: More difficult, but not substantially more difficult. Also, for many of the countries, decades of experience showed that independent monetary policy was not optimal or even good monetary policy.
|
|||
A legalized and carefully regulated market for cannabis would lead to measurably higher social welfare than a system of prohibition.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
6 |
Question A: The economic and financial sanctions against Russia are substantially limiting its ability to wage war on Ukraine.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
6 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question B: In the absence of continuing flows of Western economic aid, Ukraine's wartime economy will be substantially compromised.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A: A constitutional rule that limits the size of budget deficits that governments can run as a share of GDP is an effective way to impose discipline on a country’s public finances.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
7 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
Comment: One number for the deficit will rarely be optimal. And, within the set of sub-optimal second-best rules, there seem to be better alternatives.
|
|||
Question B: Germany’s debt brake is a substantial constraint on vital public investment in physical/digital infrastructure and the green transition.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
No Opinion |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A:The fundamental cause of Argentina’s high inflation is unfunded fiscal commitments that are being financed by the central bank.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Even if Argentina could marshal the resources to make a full switch to using US dollars for domestic transactions, it would substantially increase the volatility of Argentine GDP.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
8 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A: It is best for society if the management of publicly traded corporations only considers the impact of their decisions on customers, employees, and community members to the extent that these effects feedback to affect shareholder wealth.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
Comment: Without a mechanism for accountability and incentives in the firm that includes other new stakeholders, then adding these objectives to management would just increase managerial discretion.
|
|||
Question B: The typical chief executive officer of a publicly traded corporation is paid more than his or her marginal contribution to the firm's value.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
8 |
Uncertain |
6 |
Question A: By enabling women’s life choices about education, work and family, the contraceptive pill made a substantial contribution to closing gender gaps in the labor market for professionals.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
7 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Gender gaps in today’s labor market arise less from differences in educational and occupational choices than from the differential career impact of parenthood and social norms around men's and women’s roles in childrearing.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question C: The gender gap in pay would be substantially reduced if firms had fewer incentives to offer disproportionate rewards to individuals who work long and/or inflexible hours.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
6 |
Agree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question A: The EU's taxonomy for sustainable activities - a classification system that defines criteria for economic activities that are aligned with a net zero trajectory by 2050 and the broader environmental goals other than climate - is an effective way to steer greener investment and the energy transition by firms and financial institutions.
Details on the taxonomy are here:
https://finance.ec.europa.eu/sustainable-finance/tools-and-standards/eu-taxonomy-sustainable-activities_en
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
No Opinion |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Use of the EU taxonomy for sustainable activities is likely to stifle important innovations, including in green technology.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
No Opinion |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C: On balance, use of the taxonomy in EU directives and regulation is likely to be net beneficial to European citizens.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
No Opinion |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Fiscal rules on budget deficits and public debt levels are an essential part of a sound fiscal framework.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
6 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Since the inception of the Stability and Growth Pact, budget deficits in Europe have been measurably lower, on average, than would have been the case without common budget rules.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question C: Since the inception of the Stability and Growth Pact, the path of GDP growth in Europe has been measurably more stable than would have been the case without common budget rules.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
6 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Non-bank financial intermediaries pose a substantial threat to financial stability.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
6 |
Agree |
6 |
Question B: Regulating the leverage and liquidity of non-bank financial intermediaries would substantially improve financial stability.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
6 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: Statement is too broad to be very certain.
|
|||
Question C: Given current regulations, non-bank financial intermediaries should not have access to central bank support.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question A: A significant factor behind today’s inflation in Europe is dominant corporations in uncompetitive markets taking advantage of their market power to raise prices in order to increase their profit margins.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Disagree |
4 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
Comment: Unlikely from the start given theory; very hard to identify empirically; no compelling evidence to reject the null hypothesis of no effect.
-see background information here -see background information here -see background information here |
|||
Question B: A significant factor behind today’s inflation in some sectors of the European economy is dominant corporations in uncompetitive markets taking advantage of their market power to raise prices in order to increase their profit margins.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Disagree |
6 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: Is "some sectors" means many relevant sectors we are back at the previous question; if it means few, then this is not inflation but changes in relative prices.
|
|||
Question C: A significant factor behind today’s inflation in some sectors of the European economy (both competitive and concentrated) is distortions in the aggregate economy where supply does not meet demand.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Disagree |
7 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: Disagree with wording: supply and demand are model objects, and are always same by definition of equilibrium. Yes, some of the high inflation is due to shocks to marginal costs. But less so right now than one year ago, and only when combined with loose monetary policy.
-see background information here |
|||
Question A: If countries could impose a ban on the use of ChatGPT and similar generative AI chatbot services that is technologically effective, they would experience a measurably negative impact on national innovation.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Regardless of whether advances in AI spur productivity growth, they are likely to create deep challenges for society – in areas from labor markets to politics, and including disinformation, privacy, crime, and warfare – that will be difficult to anticipate, plan for, and contain.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
5 |
Agree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Use of artificial intelligence over the next ten years will lead to a substantial increase in the growth rates of real per capita income in the US and Western Europe over the subsequent two decades.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
9 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: While there are solid facts on the diffusion of new technologies and their impact on growth, I thought that the estimates of the speed/timing over which these materialize has very large confidence bands.
-see background information here -see background information here |
|||
Question B: Use of artificial intelligence over the next ten years will have a substantially bigger impact on the growth rates of real per capita income in the US and Western Europe over the subsequent two decades than the internet has had over the past two decades.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
8 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Preserving the financial viability of France's state pension system is better achieved by raising the effective retirement age than by raising contributions while working.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
6 |
Agree |
7 |
Question B: Preserving the financial viability of France's state pension system is better achieved by raising the effective retirement age than by reducing benefits once retired.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
6 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: Depends if focus is on efficient allowing for transfers, or if care about different groups winning or losing
-see background information here |
|||
Question A: Financial regulators in the US and Europe lack the tools and authority to deter runs on banks by uninsured depositors.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Uncertain |
7 |
Question B: Not guaranteeing uninsured deposits at Silicon Valley Bank in full would have created substantial damage to the US economy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
8 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
Comment: Very hard to asses, so I'm confidently uncertain.
|
|||
Question C: Fully guaranteeing uninsured deposits at Silicon Valley Bank substantially increases banks’ incentives to engage in excessive risk-taking.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
8 |
|
Comment: Yes, at the margin, removed further the threat of a run to discipline management, and made the call option on making a bank in a risky way more valuable. Whether quantitatively significant is harder to judge.
|
|||
Question A: The amendments to the Northern Ireland protocol agreed by the UK and the EU are unlikely to have a measurable direct impact on UK growth over the next two years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
5 |
Disagree |
5 |
|
Comment: They help the UK move on and start many other reforms it needs.
|
|||
Question B: If renewed UK-EU scientific cooperation were achieved in the wake of the Windsor framework, it would be likely to have a measurable positive impact on UK growth over the next five years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
Comment: Science and education are two of the few world-leading industries in the country
|
|||
Question A: Adam Smith’s metaphor of the invisible hand has been foundational to the development of modern economic theory.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
8 |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Adam Smith’s metaphor of the invisible hand has been commonly misinterpreted as advocacy for pure laissez-faire capitalism.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
4 |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Loosening regulations on state aid to allow targeted incentives for companies in certain sectors will substantially improve the EU’s relative attractiveness for corporate investment.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
5 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: I worry that most of the effect will be diversion of investment across EU states, so the effects will be small for the EU on aggregate.
-see background information here |
|||
Question B: Loosening regulations on state aid will give a substantial advantage to the economies of EU members with stronger public finances.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
4 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question C: Even if looser regulations on state aid are temporary, they risk permanent damage to the EU’s longstanding competition policy regime.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
5 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: My impression is that the literature in the last two decades has found several examples of industrial policies working. Of course, sometimes is not working on average
-see background information here -see background information here -see background information here -see background information here |
|||
Question A: Without government intervention, take-up of electric vehicles will be substantially less than is desirable to reduce carbon emissions.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
3 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: I'm far from an expert in this area, and there are effects on both directions, but Im relying my assessment on a widely-cited paper in this area and a recent survey.
-see background information here -see background information here |
|||
Question B: To encourage greater take-up of electric vehicles, public expenditure on infrastructure to support them (such as charging stations) is likely to be more cost-effective than providing equivalent amounts as tax credits/purchase rebates for buyers.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
5 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: Focussing on the dynamic benefits, rather the static losses, it seems that infrastructure would be more effective at the demand-pull and network effects that this paper persuasively emphasizes.
-see background information here |
|||
Question A: Network externalities give Twitter an incumbent advantage that will slow substantially the migration of users who would prefer alternative platforms.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
6 |
Agree |
7 |
Question B: As of now, there needs to be more government regulation around Twitter’s content moderation and personal data protection.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
4 |
Agree |
5 |
|
Comment: Depends on which type of regulation. Some forms of government regulation of media content are tools for totalitarianism.
-see background information here |
|||
Question A: The carbon border adjustment mechanism will ensure that the European Union’s green objectives are not undermined by the relocation of EU production in the sectors under the mechanism to non-EU countries with less ambitious climate policies (‘carbon leakage').
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: To the extent that the carbon border adjustment mechanism is effective in reducing emissions and carbon leakage, it will impose substantial costs on the economies of poorer countries.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Research on the nature and impact of bank runs has made it possible to limit the occurrence of financial crises and the economic damage they cause.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
8 |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Despite repeated reforms of financial regulation (and macroprudential policies in some countries), there will always be occasional financial crises.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
8 |
Agree |
8 |
|
Comment: We can prevent some run-ups, reduce the collapses, and boost the recoveries, but the state of our knowledge is quite far from eliminating them entirely.
-see background information here |
|||
Question A: The UK’s removal of the cap on bankers' bonuses (introduced by the EU in 2014 and which limits payouts to two times annual base salary) will provide a measurable boost to the country’s economic growth.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
7 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
Comment: Link to growth is tenuous, and hard to see how it could be very significant (and therefore measurably statistically significantly different from zero). May still be a good policy, however.
|
|||
Question B: Removing the cap on bankers' bonuses will measurably enhance the global competitiveness of the UK’s financial services sector.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
6 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: In an industry where asymmetric information and incentives are important, contracts will adjust to this change. It might work, but could backfire.
|
|||
Question C: Removing the cap on bankers' bonuses will pose a measurable risk to financial stability in the UK.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
7 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
Comment: Effect is positive, as encourages more risk taking, but contracts all adjust, and unclear that this translates into more likely systemic crises.
|
|||
Question A: A price cap imposed by the G7/EU countries on purchases of Russian oil and oil-related products (and which applies to all importers of Russian oil using Western trade infrastructure, shipping, and insurance) would be an effective measure to reduce the flow of revenues to Russia.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
6 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: Effective to reduce the flow of revenues to Russia, but unclear how large. Depends, in the short run on response of non-G7/EU government, and in the long-run on entry into market of non-G7/EU traders/shippers/financiers.
-see background information here |
|||
Question B: The oil price cap imposed by the G7/EU countries will not have a substantial effect on the world oil price (such as the Brent crude benchmark).
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: Effect is on infra-marginal.
|
|||
Question A: The increasing share of income and wealth among the richest people in a number of advanced countries is giving significantly more political power to the wealthy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
4 |
Agree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question B: The increasing share of income and wealth among the richest people in a number of advanced countries is having a significantly negative effect on intergenerational social mobility.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
3 |
Agree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question C: The increasing share of income and wealth among the richest people in a number of advanced countries is a major threat to capitalism.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
1 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question A: A windfall tax on the excess profits of large oil and gas companies – with the revenue rebated to households – would be an efficient way to provide temporary relief for the average household in European countries from rising energy costs.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
3 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: Yes in principle, but highly uncertain effect on expectations of future taxes for lucky industries, subsidies when energy prices fall, etc.
|
|||
Question B: Fiscal measures putting a cap on consumer energy prices would be a more appropriate immediate response to increased inflation in the euro area than raising interest rates.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Disagree |
8 |
Strongly Disagree |
8 |
Stablecoins that are not fully backed by either central bank reserves or government securities with minimal price volatility are inherently vulnerable to runs.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
High tariffs imposed by the European Union on imports of Russian natural gas would be an effective measure to reduce the flow of revenues to Russia while limiting disruption to supplies to Europe.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
7 |
Agree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Rather than using second-round runoffs to settle elections in which no candidate wins a first-round majority, the overall preferences of the electorate would be better reflected by using a single round with ranked-choice voting, in which voters are instructed to rank all of the candidates.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A:Rising energy prices suggest that the European Central Bank and the Federal Reserve will have to increase interest rates faster than they intended to before the invasion.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Uncertain |
8 |
|
Comment: Ceteris paribus, yes. How much / how fast requires careful analysis.
-see background information here |
|||
Question B: Increased public spending by European countries to accommodate larger defense budgets, migration inflows and accelerated investment in alternative energy sources would be better financed mostly through taxes, rather than debt.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
7 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: Depends. Unclear for instance how permanent/transitory each of these are
|
|||
Question C: Economic damage from the shock to global commodity markets will fall disproportionately hard on low- and middle-income countries.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
6 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: Very heterogeneous group, including some large net exporters and net importers of different commodities.
-see background information here |
|||
Question A:The fallout from the Russian invasion of Ukraine will be stagflationary in that it will noticeably reduce global growth and raise global inflation over the next year.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
6 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: The economic and financial sanctions already implemented will lead to a deep recession in Russia.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
6 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question C: Targeting the Russian economy through a total ban on oil and gas imports carries a high risk of recession in European economies.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: But it is worth it.
|
|||
Question D: Weaponizing dollar finance is likely to lead to a significant shift away from the dollar as the dominant international currency.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
7 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
Comment: It is hard to jumpstart alternatives, and then to make them grow
-see background information here |
|||
Question A:High volatility in the prices of crypto assets such as Bitcoin, Dogecoin, and Ethereum largely reflects movements in investor sentiment rather than news about potential sources of fundamental value (such as possible applications, or use in illicit transactions).
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: This is true for stocks as well (Campbell-Shiller). Even more so for something as flimsy as crypto
-see background information here |
|||
Question B: Given existing regulation of the financial system, as crypto assets grow in value and become more connected to the rest of the system, the fluctuations in their valuations will pose a serious risk to financial stability in advanced economies.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Disagree |
7 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
Comment: Volatility in asset prices may cause instability if associated with leverage. Not the case for crypto now (and hope it'll not become so)
|
|||
Question C: Private unbacked crypto assets serve no important economic purpose.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
4 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
Comment: Assets can be combined in so many ways to shift risk.
|
|||
Question A:Firms’ incentives to reduce costs by sourcing inputs and products abroad have caused many European industries to become more vulnerable to supply chain disruptions.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
7 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: This is often stated, but I have not seen hard evidence actually backing it.
|
|||
Question B: Private firms have inadequate incentives to make investments to reduce the risk that disruptions in the supply of imports will cause shortages and raise domestic prices.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
7 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: What is the missing market? The firm would benefit greatly from being the only supplier when other firms cannot.
|
|||
Question C: Prioritisation of efficiency over resilience in global supply chains makes current disruptions likely to continue beyond 2022.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
7 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: The existence of a tradeoff between efficiency and resilience is not clear to me.
|
|||
Question A:Given the centrality of semiconductors to the manufacturing of many products, securing reliable supplies should be a key strategic objective of EU and national policy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
No Opinion |
Agree |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Europe’s small role in global semiconductor production is a direct result of insufficient private investment in high-tech innovation.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
No Opinion |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C: Public support at EU and national level for investment along the value chain for semiconductors, including production, would be the most effective way to ensure security of supply.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
No Opinion |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A:Even without renewed Covid-19 restrictions, uncertainty about the health threat from the Omicron variant is likely to deliver a significant hit to economic activity from now through the first half of 2022.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
6 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question B: If world vaccine supply continues to be limited, global social welfare would rise by more if those vaccines were made widely available across Africa (with support for effective delivery) rather than accelerating booster vaccinations in rich countries.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
7 |
Agree |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question C: Imposing travel bans on countries where new Covid-19 variants are discovered will make it less likely that countries will reveal new variants to the rest of the world.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
4 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Voluntary national targets are unlikely to be an effective mechanism for achieving sharp reductions in greenhouse gas emissions.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: We achieved significant reductions with mostly national policies adopted by rich countries. But tragedy of commons means likely too little
-see background information here |
|||
Question B: Agreement on a significant global price floor for all carbon emissions would be an effective step towards achieving sharp reductions in emissions.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
5 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: Only if well designed. Countries have different market structures for trading/auctioning carbon, and reserve prices can backfire in some.
-see background information here |
|||
Question C: Green innovation in the private sector would be strongly stimulated by a substantial increase in public spending on R&D for climate change mitigation and adaptation.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: Public R&D spending tends to crowd in private R&D spending.
-see background information here |
|||
Question A: The introduction of natural experiments to economic analysis of the labor market and related areas has led to a more precise understanding of cause and effect.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Agree |
8 |
|
Comment: As explained by Nobel prize committee in its, as usual, very useful report.
-see background information here |
|||
Question B: The ‘credibility revolution’ in empirical economics has improved our understanding of a number of public policy issues, including education, immigration and the minimum wage.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
8 |
Agree |
8 |
|
Comment: Definitely improved. Of course, one would hope that progress had been even larger and more decisive. But no doubts on the sign of progress.
|
|||
Question C: In pursuit of credible research designs, researchers often seek good answers instead of good questions.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
7 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: Within set of good answers, they pick the better questions. Researchers trade off the two, unclear that they do so sub-optimally.
|
|||
Question A: A mandate for public companies to provide climate-related disclosures (such as their greenhouse gas emissions and carbon footprint) would provide financially material information that enables investors to make better decisions.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: A mandate for public companies to provide climate-related disclosures would induce them to reduce their climate impact significantly.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: The current combination of US fiscal and monetary policy poses a serious risk of prolonged higher inflation.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
Comment: I put the odds of inflation above 4% on average 5y5y at 10-15%. That is too high.
|
|||
Question B: Current EU and national fiscal policy plans are likely to leave European output below potential a year from now.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
8 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
Comment: Still hard to gauge what is potential post pandemic (e.g., in tourism, which is a big share of Europe GDP)
|
|||
Question A:The introduction of even small trade frictions between neighboring countries can result in significant economic damage, particularly to smaller exporting firms.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
7 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: "Significant" is in the eye of the beholder, but literature has quantified multiple relevant channels
-see background information here -see background information here |
|||
Question B: A national economic boom based on natural resources is likely to harm other sectors of the economy, particularly manufacturing firms.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
7 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: It seems to depend on the country's circumstances, and especially on the policies adopted in response.
-see background information here -see background information here -see background information here |
|||
Question A: A global minimum corporate tax rate would limit the benefits to companies of shifting profits to low-tax jurisdictions without biasing where they invest.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
5 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: All taxes (or almost all) bias investment decisions.
|
|||
Question B: An international tax system in which the major advanced economies set a minimum rate on corporate income is achievable.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question C: A global corporate tax system that is based on the location of final consumers would be more efficient than one based on the location of corporate headquarters and production facilities.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
5 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Under a fixed exchange rate and fully liberalized capital flows, a country loses domestic control of monetary policy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Agree |
8 |
|
Comment: The question said "fully liberalized". Understanding that as meaning that UIP holds exactly, then this is a theorem
|
|||
Question B: For emerging and developing economies open to the world capital market, a flexible exchange rate confers little advantage over a pegged exchange rate in terms of economic stability.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Disagree |
8 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question C: The key feature making the US a more natural optimum currency area than the euro area is higher labor mobility.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
6 |
Disagree |
8 |
|
Comment: Other features matter as well, for instance the fiscal union or the relative efficiency of the allocation of capital flows.
-see background information here |
|||