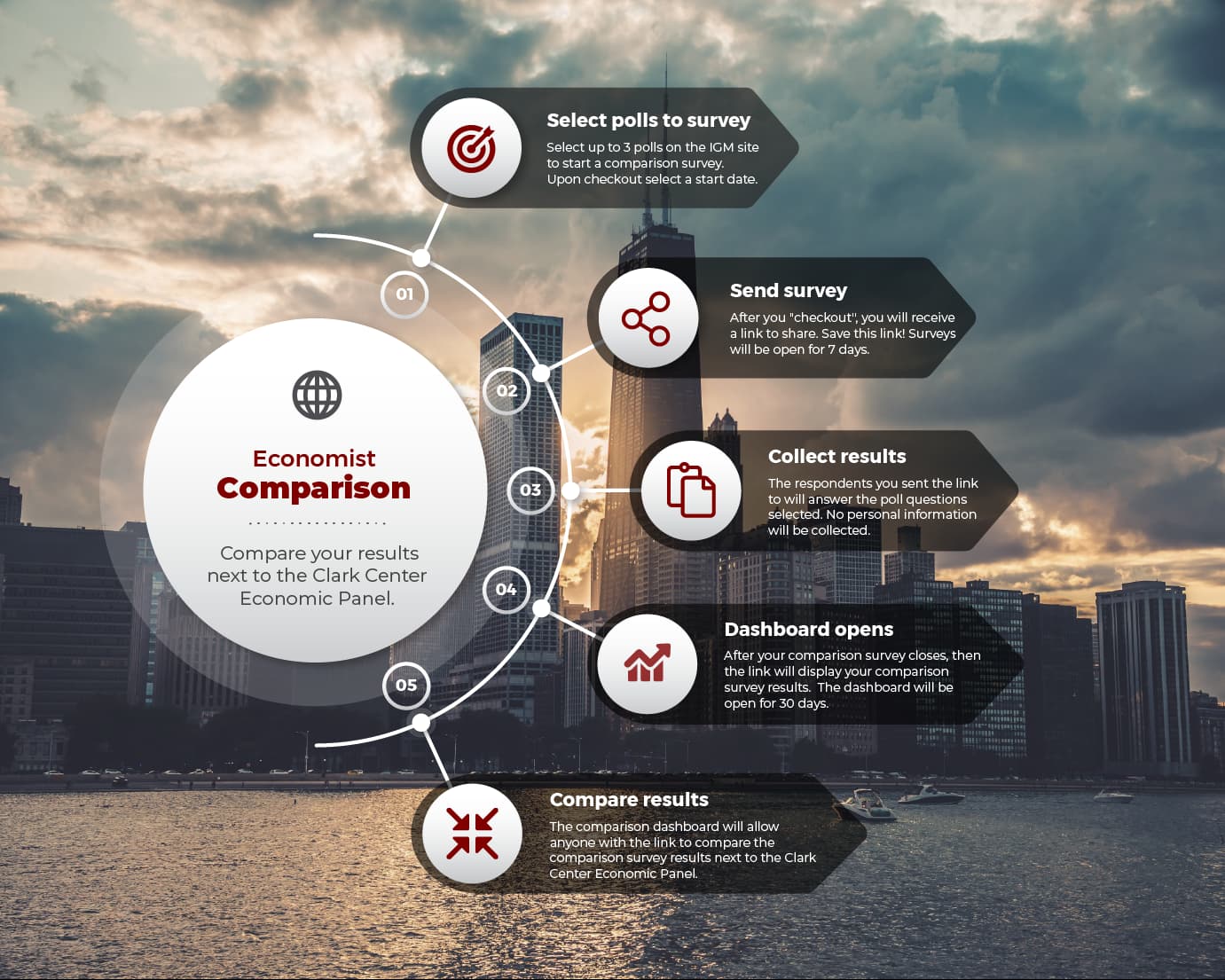
About
- Savings Banks Foundations and Swedbank Chair in Macroeconomics
- Director of the CEPR Program in International Macroeconomics (2006-11), Fellow of the Econometric Society (since 2006)
- Wallenberg Scholar (2011), Söderberg Prize (2007)
- Member of the Prize Committee for The Sveriges Riksbank Prize in Economic Sciences in Memory of Alfred Nobel (2003-13 and 2017-19), Chair from 2011-13
Voting History
Question A:Rising inequality is straining the health of liberal democracy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
Question B: Enacting more redistributive expenditures and policies would be likely to limit the rise of populism in Europe.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
Question C: European governments should allocate more resources to policies that would be likely to limit the rise of populism in Europe, even if it means higher public debt or lower public spending in other areas.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
Question A:At this point, there is little that the European Central Bank can do to increase or maintain output in the Eurozone.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
Question B: When the economy is operating below its potential, larger fiscal deficits are likely to increase demand and output.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Comment: If the government’s money isn’t wasted.
|
|||
Question C: When the economy is operating below its potential and monetary policy is at the effective lower bound, fiscal policy should prioritize increasing output over decreasing public debt.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Comment: Ok if debt position is not in danger zone.
|
|||
Question A:Selecting candidates for membership of the ECB Executive Board based primarily on nationality ahead of competence is likely to have a negative effect on the quality of monetary policy in the Eurozone.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Comment: To maintain broad support among euro member countries representativeness may also be relevant.
|
|||
Question B: Although the central bank can never be an entirely technocratic institution, the selection process for the ECB President and members of the Executive Board is significantly worsened by intergovernmental trade-offs involving appointments to other European institutions.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
On bids for infrastructure projects, the average European would be better off if Europe’s governments favored European firms over Chinese firms (or firms from any other country with non-profit-related geopolitical strategies) — even if it means sometimes choosing a higher-cost bidder.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Comment: I take it that the comparison includes all components (quality, on-time delivery, etc). Helping inefficient companies doesn’t improve them.
|
|||
Question A: Breaking the “doom loop” — a negative spiral that can result when banks hold sovereign bonds and governments bail out banks — would increase the stability of European economies in the event of another financial crisis.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
Question B: Regulators should try to break the doom loop by assigning positive risk weights — in calculating banks’ capital requirements — to banks’ holdings of domestic and other Eurozone sovereign bonds.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
Question C: Breaking the doom loop would impose substantial costs on powerful political constituencies.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||