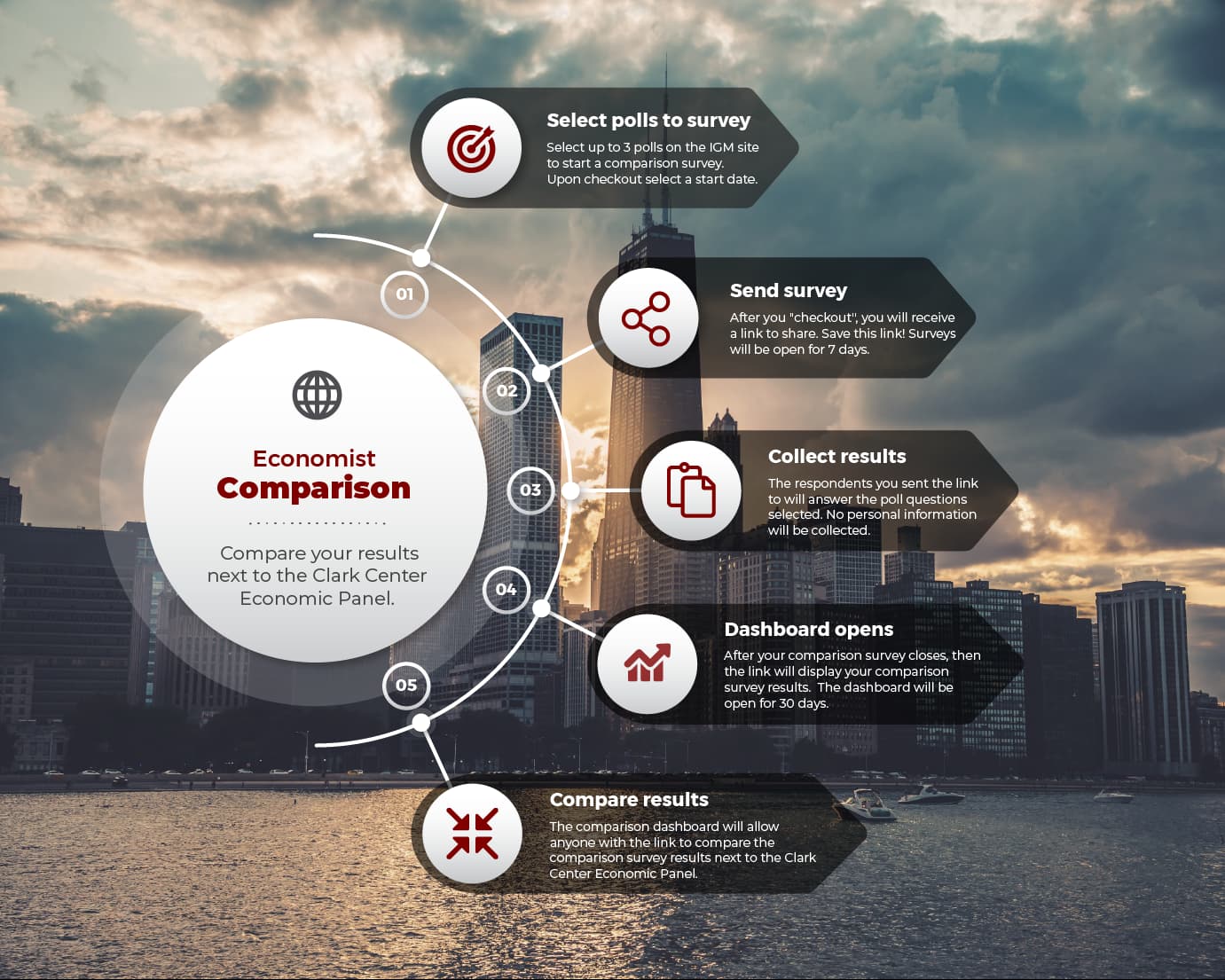
About
- C. Fred Bergsten Senior Fellow, Peterson Institute
- Chief Economist, International Monetary Fund (2008-15)
- President-elect of the American Economic Association (2016- present)
- Officier de la Légion d’Honneur (2008)
Voting History
Question A: The reductions in Western programs of development assistance will have no measurable effects on GDP growth in the recipient countries over the next five years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
1 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
Comment: one would have to know much more about the various programs that have been stopped. But, if not about growth, probably about diseases, mortality...
|
|||
Question B: The reductions in Western programs of development assistance will have substantially negative effects on the most vulnerable people in the recipient countries over the next five years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
3 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: based on limited knowledge, it looks bad for some vulnerable groups.
|
|||
Question C: Development assistance motivated by the potential benefits for the donors in terms of prosperity and security is measurably more effective in promoting GDP growth in recipient countries than aid based on humanitarian or other moral principles.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
10 |
Disagree |
5 |
|
Comment: If the statement is really about "benefits for the donors" in terms of their own prosperity, this is an amazingly stupid statement.
|
|||
Question A: Matching US import tariffs to the tariffs, value-added taxes and non-tariff barriers imposed on US goods by other countries would substantially reduce the US trade deficit.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
8 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
Comment: conclusion is more general: Tariffs on any sort have limited effects on the trade balance.
|
|||
Question B: The threat of retaliation against the imposition of higher tariffs on a country’s exports substantially lowers the probability of a trade war.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
7 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: reciprocal tariffs will not lead the Trump administration to decrease their own. And they may lead it to double down.
|
|||
Question C: In the event that the threat of retaliation does not deter the imposition of tariffs, the economies of countries subject to higher tariffs on their exports would be measurably better off by responding with targeted tariffs on imports from the first mover.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
7 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: complex, depending on the nature of the countermeasures, including export restrictions. A general reciprocal tariff probably makes you even worse off.
|
|||
Question A: The wave of immigration to Germany after 2015 (and up to the Russian invasion of Ukraine) has been a net positive for the country's economy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
4 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Immigration to EU countries has been a net positive for government finances, adding substantially more in tax revenues than the increased costs associated with integration of immigrants.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
4 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question C: Given Europe's low and falling fertility rates (from seven million births per year in 1960 to four million today), maintaining its position as a world economic power will require increased immigration over the medium term.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
6 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: two points. Can sustain growth per capita without immigration. Second, politically unrealistic to hope that immigration will offset domestic demographics.
|
|||
Question A: Putting America First in International Environmental Agreements: https://www.whitehouse.gov/presidential-actions/2025/01/putting-america-first-in-international-environmental-agreements/
'In recent years, the United States has purported to join international agreements and initiatives that do not reflect our country's values or our contributions to the pursuit of economic and environmental objectives... The United States Ambassador to the United Nations shall immediately submit formal written notification of the United States' withdrawal from the Paris Agreement under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change.'
US withdrawal from the Paris climate agreement will deliver a measurable boost to the country's economic growth over the next four years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
4 |
Disagree |
5 |
|
Comment: sign is probably right. But "measurable" may be excessive
|
|||
Question B: US withdrawal from the Paris climate agreement will have a measurably negative impact on international progress on mitigation of global warming.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: for mechanical reasons, and I do not see other countries doing sufficiently more to offset.
|
|||
Question A: A baseline US tariff of 10% on all European imported goods would have substantially damaging economic consequences for many countries in Europe.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: the effects would depend very much on the degree to which the tariffs are offset by a euro depreciation
|
|||
Question B: Rather than responding to threatened tariffs with retaliatory measures, unilaterally opening EU markets to US exports would deliver better outcomes for European industry.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
7 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: i think the structure of the game is a prisoner's dilemma. Once the US puts tariffs, it is very likely that the best response is to do the same.
|
|||
Question C: Disruptions to global supply chains from new tariffs and trade wars will lead to measurably slower global growth over the next five years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: leaving aside the permanent efficiency losses from less trade, the reallocation implied by the tariffs is likely to have substantial adverse effects in the short run
|
|||
Question A: The likely need for increased European public investment in defense should come with substantial reallocations of public budgets at the national and EU levels.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: evidence of substantial duplication
|
|||
Question B: Greater use of joint EU-level procurement of military equipment and defense research/innovation would promote substantially enhanced capacity in Europe's defense industry.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question C: Increased defense spending would deliver a measurable boost to economic growth in Europe over the next five years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
7 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: depends how it is financed...
|
|||
On the basis of current climate policy commitments and potential technology and market responses, my current best estimate for global warming is that average global temperatures by 2100 will rise to no more than 2.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
10 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: I do not know enough even to have a guess. Technological progress is surprisingly fast. But political support and funding is, as would be expected, not sufficient. Which of these two forces will dominate, I just do not know.
|
|||
Question A: A period of high inflation is substantially more electorally damaging to incumbent governments in advanced countries than a period of high unemployment.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
6 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: clearly true this time. but, as an eternal truth, not obvious.
|
|||
Question B: Voters are more likely to punish incumbents for what they perceive as poor national economic performance than they are to reward incumbents for a good economy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
3 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: Sounds plausible. But I have not seen any estimate of this asymmetry.
|
|||
Question A: The institutions of society - such as constitutions, laws, judiciaries, and property rights - substantially shape economic decisions, policies, and outcomes.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
6 |
Strongly Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question B: On average and over the long term, democracies deliver substantially better economic growth than other forms of government.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
4 |
Agree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question C: Countries where democracy and the rule of law are weakened are likely to experience measurable damage to their economic performance.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
5 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Current enforcement of competition policy in Europe is not working to promote innovation and growth.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
6 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: it may constrain firms and thus limit the GDP growth rate, but it may yield "better" growth.
|
|||
Question B: European Union bureaucracy and regulations are a substantial constraint on innovation in Europe.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
5 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: similar answer. The surely constrain firms, but, in large part, for the better. (They may be too heavy, even accepting the goal)
|
|||
Question C: The conduct of the dominant US tech companies in European markets (including lobbying and acquisition of start-ups and competitors) is a substantial constraint on innovation in Europe.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
4 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: not clear why the "in Europe" part.
|
|||
Question A: In pursuing social and environmental initiatives, the average public company generates more benefits than costs in terms of profits.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
5 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: The financial rewards come from image improvement, more and more enthusiastic consumers. This is likely to be marginal in most cases.
|
|||
Question B: In pursuing social and environmental initiatives, public companies would benefit from a measurably lower cost of capital.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
7 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: I am skeptical as to how many investors, especially the large ones will be willing to lend at lower rates. Again, likely to be a marginal effect
|
|||
Question C: There are substantial social benefits when managers of public companies make choices that account for the impact of their decisions on customers, employees, and community members beyond the effects on shareholders.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: Usual distinction between social and private benefits
|
|||
Question A: US antitrust investigations of the dominant firms in artificial intelligence are warranted by the need to foster competition and innovation in the technologies.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
4 |
Agree |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Seeking to slow the pace of artificial intelligence use and implementation would be a more effective means of assessing potential harms from the technologies than market deployment and ex post assessment.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
4 |
Uncertain |
4 |
|
Comment: I am not sure I know what slowing down the pace of AI use means in practice, and how it can be enforced.
|
|||
Question A: The proposed US tariffs on Chinese EVs would lead to measurably higher employment in the US automotive industry over the next five years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: and us consumers paying substantially more.
|
|||
Question B: The proposed US tariffs on Chinese EVs would measurably slow the adoption of green technology by consumers.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
5 |
|
Comment: higher prices for EVs, less adoptions.
|
|||
Question C: Unless the EU matches the proposed US tariffs on Chinese EVs, there would be measurably lower employment in Europe's automotive industry over the next five years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
7 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: no need to match. Higher tariffs but not 100%, and no restriction on Chinese FDI in Europe.
|
|||
Question A: Greater integration of national markets for financial services, energy and telecommunications would give a measurable boost to Europe’s GDP over the next ten years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
5 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: These are fairly integrated markets already. It can be improved, but I would not expect miracles.
|
|||
Question B: The potential benefits for GDP from loosening European merger rules to allow greater consolidation within the single market would outweigh the potential harm to consumers from weaker competition.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
5 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: can only be assessed case by case.
|
|||
Question A:Creation of a more unified capital market in Europe - with a common pool of capital, a single rule book and a strengthened European Securities and Markets Authority, comparable to the US Securities and Exchange Commission – would lead to a substantial shift in the balance of companies listing their shares in the EU vis-a-vis the US.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
4 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Creation of a more unified capital market in Europe - with a common pool of capital, a single rule book and a strengthened European Securities and Markets Authority, comparable to the US Securities and Exchange Commission – would substantially increase the availability of funding for start-ups and growing companies across the EU.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
4 |
Agree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question A: The European Union's AI Act was approved by the European Parliament in March 2024: https://artificialintelligenceact.eu/the-act/
The EU's legislation to regulate artificial intelligence is likely to put European technology firms at a substantial disadvantage to their competitors elsewhere in the world.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
3 |
Disagree |
5 |
|
Comment: having read (part) of the regulation: the complexity of the tasks needed to satisfy the regulation may lead some entrepreneurs to move outside the EU.
|
|||
Question B: By providing a clear set of rules, the EU's legislation on artificial intelligence is likely to enhance research and innovation by firms building the new technology.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
3 |
Disagree |
4 |
|
Comment: this is the other side of the coin. a measure with costs and benefits...
|
|||
Question A: Europe’s economic growth performance over the last 25 years has been measurably better than it would have been in the absence of the single currency.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: It has avoided what would likely have been exchange rate crises in the weaker countries. But it has made normal macroeconomic adjustment substantially harder, in the absence of country specific monetary policy and exchange rate.
|
|||
Question B: With euro area member states having given up their ability to carry out independent monetary policy, it is substantially more difficult for them to respond effectively to country-specific macroeconomic disturbances.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
1 |
Uncertain |
8 |
|
Comment: this was half of my answer to the first question.
|
|||
A legalized and carefully regulated market for cannabis would lead to measurably higher social welfare than a system of prohibition.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
4 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: the issue is whether increased use of cannabis would increase the demand for harder drugs.
|
|||
Question A: The economic and financial sanctions against Russia are substantially limiting its ability to wage war on Ukraine.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
4 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: On technology, Russia seems to be finding ways of getting it anyway. On oil, it also seems to be finding people who are willing to help. Still, there must be some effect on the economy, from higher costs of tech, and lower oil prices.
|
|||
Question B: In the absence of continuing flows of Western economic aid, Ukraine's wartime economy will be substantially compromised.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: This seems fairly obvious.
|
|||
Question A: A constitutional rule that limits the size of budget deficits that governments can run as a share of GDP is an effective way to impose discipline on a country’s public finances.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
9 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
Comment: If the rule is espected, it does indeed impose fiscal discipline. At the potential cost of the potential loss of fiscal policy as a tool for macro stabilisation.
|
|||
Question B: Germany’s debt brake is a substantial constraint on vital public investment in physical/digital infrastructure and the green transition.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: There is a trade off between debt reduction and public investment, be it defense or green spending. The debt brake may well force choosing the wrong point on the trade off curve.
|
|||
Question A:The fundamental cause of Argentina’s high inflation is unfunded fiscal commitments that are being financed by the central bank.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
9 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Even if Argentina could marshal the resources to make a full switch to using US dollars for domestic transactions, it would substantially increase the volatility of Argentine GDP.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
9 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
Comment: The economy is very volatile under the existing system. It would be volatile in a different way, not being able to use m policy or the e rate for stabilization.
|
|||
Question A: It is best for society if the management of publicly traded corporations only considers the impact of their decisions on customers, employees, and community members to the extent that these effects feedback to affect shareholder wealth.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
7 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
Comment: we have moved away from "just max profit". But we realize that this is dangerous territory. Probably better to incentivize better social behavior through rules and regulation, again with great care.
|
|||
Question B: The typical chief executive officer of a publicly traded corporation is paid more than his or her marginal contribution to the firm's value.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
7 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: The MPL of a good CEO can be very substantial.
|
|||
Question A: By enabling women’s life choices about education, work and family, the contraceptive pill made a substantial contribution to closing gender gaps in the labor market for professionals.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
2 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Gender gaps in today’s labor market arise less from differences in educational and occupational choices than from the differential career impact of parenthood and social norms around men's and women’s roles in childrearing.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
3 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question C: The gender gap in pay would be substantially reduced if firms had fewer incentives to offer disproportionate rewards to individuals who work long and/or inflexible hours.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
3 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: what are those "incentives"?
|
|||
Question A: The EU's taxonomy for sustainable activities - a classification system that defines criteria for economic activities that are aligned with a net zero trajectory by 2050 and the broader environmental goals other than climate - is an effective way to steer greener investment and the energy transition by firms and financial institutions.
Details on the taxonomy are here:
https://finance.ec.europa.eu/sustainable-finance/tools-and-standards/eu-taxonomy-sustainable-activities_en
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
No Opinion |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Use of the EU taxonomy for sustainable activities is likely to stifle important innovations, including in green technology.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
No Opinion |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C: On balance, use of the taxonomy in EU directives and regulation is likely to be net beneficial to European citizens.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
No Opinion |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Fiscal rules on budget deficits and public debt levels are an essential part of a sound fiscal framework.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
Comment: I have a semantic issue with "rules". These could be, as I have argued, the use of a debt sustainability analysis, or institutional arrangements, not necessarily a set of hard numbers
|
|||
Question B: Since the inception of the Stability and Growth Pact, budget deficits in Europe have been measurably lower, on average, than would have been the case without common budget rules.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question C: Since the inception of the Stability and Growth Pact, the path of GDP growth in Europe has been measurably more stable than would have been the case without common budget rules.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
8 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
Comment: Plenty of procyclical policy as a result of bad rules.
|
|||
Question A: Non-bank financial intermediaries pose a substantial threat to financial stability.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
4 |
Agree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Regulating the leverage and liquidity of non-bank financial intermediaries would substantially improve financial stability.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
4 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question C: Given current regulations, non-bank financial intermediaries should not have access to central bank support.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
4 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: time consistency issues in full play here
|
|||
Question A: A significant factor behind today’s inflation in Europe is dominant corporations in uncompetitive markets taking advantage of their market power to raise prices in order to increase their profit margins.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
6 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question B: A significant factor behind today’s inflation in some sectors of the European economy is dominant corporations in uncompetitive markets taking advantage of their market power to raise prices in order to increase their profit margins.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
6 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question C: A significant factor behind today’s inflation in some sectors of the European economy (both competitive and concentrated) is distortions in the aggregate economy where supply does not meet demand.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
7 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: I object to distortions. In a competitive market with inelastic demand, a restriction on supply increases profits. Nothing to do with market power or distortions
|
|||
Question A: If countries could impose a ban on the use of ChatGPT and similar generative AI chatbot services that is technologically effective, they would experience a measurably negative impact on national innovation.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: the premise of the question is wrong. there cannot be an effective ban on the use of chatgpt or AI in general.
|
|||
Question B: Regardless of whether advances in AI spur productivity growth, they are likely to create deep challenges for society – in areas from labor markets to politics, and including disinformation, privacy, crime, and warfare – that will be difficult to anticipate, plan for, and contain.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: this is the historical experience with gpts...
|
|||
Question A: Use of artificial intelligence over the next ten years will lead to a substantial increase in the growth rates of real per capita income in the US and Western Europe over the subsequent two decades.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
7 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: we have learned that what appears to be tech breakthroughs do not always lead to increases in measured tfp...
|
|||
Question B: Use of artificial intelligence over the next ten years will have a substantially bigger impact on the growth rates of real per capita income in the US and Western Europe over the subsequent two decades than the internet has had over the past two decades.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
7 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: for the same reason as the answer to the earlier question. We have a hard time assessing what the effect of the net was on pty. We must be careful about predicting the effect of AI.
|
|||
Question A: Preserving the financial viability of France's state pension system is better achieved by raising the effective retirement age than by raising contributions while working.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: It is a matter of social preferences, and whichever way it is done is fine with me.
|
|||
Question B: Preserving the financial viability of France's state pension system is better achieved by raising the effective retirement age than by reducing benefits once retired.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: same answer. matter of social preferences, and initial conditions. If retirees are perceived as being better off than those who work, fairness argument may suggest some adjustment of benefits
|
|||
Question A: Financial regulators in the US and Europe lack the tools and authority to deter runs on banks by uninsured depositors.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
Comment: This is true by definition
|
|||
Question B: Not guaranteeing uninsured deposits at Silicon Valley Bank in full would have created substantial damage to the US economy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
Comment: The SVB run made salient an issue that uninsured depositors had probably not focused on, and not bailing out would probably have led to large runs on other banks.
|
|||
Question C: Fully guaranteeing uninsured deposits at Silicon Valley Bank substantially increases banks’ incentives to engage in excessive risk-taking.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
8 |
|
Comment: Full insurance is not desirable. There are good reasons to increase the threshold, say to protect payroll for example, but it has to come with additional regulation and surveillance.
|
|||
Question A: The amendments to the Northern Ireland protocol agreed by the UK and the EU are unlikely to have a measurable direct impact on UK growth over the next two years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Disagree |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question B: If renewed UK-EU scientific cooperation were achieved in the wake of the Windsor framework, it would be likely to have a measurable positive impact on UK growth over the next five years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
6 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
Comment: . Not first order anyway and 5 years is likely too short to see measurable effects
|
|||
Question A: Adam Smith’s metaphor of the invisible hand has been foundational to the development of modern economic theory.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
10 |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Adam Smith’s metaphor of the invisible hand has been commonly misinterpreted as advocacy for pure laissez-faire capitalism.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
9 |
Agree |
8 |
|
Comment: There are few truly competitive markets in modern economies.
|
|||
Question A: Loosening regulations on state aid to allow targeted incentives for companies in certain sectors will substantially improve the EU’s relative attractiveness for corporate investment.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: Good for Europe, but not necessarily good for the world
|
|||
Question B: Loosening regulations on state aid will give a substantial advantage to the economies of EU members with stronger public finances.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: arithmetically so
|
|||
Question C: Even if looser regulations on state aid are temporary, they risk permanent damage to the EU’s longstanding competition policy regime.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: same issue: what are the new rules of the international trade game?
|
|||
Question A: Without government intervention, take-up of electric vehicles will be substantially less than is desirable to reduce carbon emissions.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
6 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: the question is ambiguous. Carbon tax or equivalent surely needed. Question is what beyond that? Public infrastructure (EV plugging stations)?
|
|||
Question B: To encourage greater take-up of electric vehicles, public expenditure on infrastructure to support them (such as charging stations) is likely to be more cost-effective than providing equivalent amounts as tax credits/purchase rebates for buyers.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
7 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: Both are needed, and neither will be fully achieved by the private sector on its own.
|
|||
Question A: Network externalities give Twitter an incumbent advantage that will slow substantially the migration of users who would prefer alternative platforms.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: This is something that we are all experiencing...
|
|||
Question B: As of now, there needs to be more government regulation around Twitter’s content moderation and personal data protection.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
5 |
Agree |
5 |
|
Comment: Twitter has incentives to get clicks, and thus to allow extreme views and intense, polarizing, discussions. Not the same as optimizing distribution of information
|
|||
Question A: The carbon border adjustment mechanism will ensure that the European Union’s green objectives are not undermined by the relocation of EU production in the sectors under the mechanism to non-EU countries with less ambitious climate policies (‘carbon leakage').
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question B: To the extent that the carbon border adjustment mechanism is effective in reducing emissions and carbon leakage, it will impose substantial costs on the economies of poorer countries.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
7 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: it depends on what measures they themselves take to limit emissions.
|
|||
Question A: Research on the nature and impact of bank runs has made it possible to limit the occurrence of financial crises and the economic damage they cause.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Despite repeated reforms of financial regulation (and macroprudential policies in some countries), there will always be occasional financial crises.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question A: The UK’s removal of the cap on bankers' bonuses (introduced by the EU in 2014 and which limits payouts to two times annual base salary) will provide a measurable boost to the country’s economic growth.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
4 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
Comment: i am skeptical it will substantially improve bankers' quality
|
|||
Question B: Removing the cap on bankers' bonuses will measurably enhance the global competitiveness of the UK’s financial services sector.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
4 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: i suspect the effect is marginal.
|
|||
Question C: Removing the cap on bankers' bonuses will pose a measurable risk to financial stability in the UK.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
4 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
Comment: again, marginal effect and better bankers do not necessarily mean less risk.
|
|||
Question A: A price cap imposed by the G7/EU countries on purchases of Russian oil and oil-related products (and which applies to all importers of Russian oil using Western trade infrastructure, shipping, and insurance) would be an effective measure to reduce the flow of revenues to Russia.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
5 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: A well designed price cap, just such as to give Russia the incentive to sell at the cap rather than just stop selling. Want to affect revenues, not quantities sold. Hard to do right.
|
|||
Question B: The oil price cap imposed by the G7/EU countries will not have a substantial effect on the world oil price (such as the Brent crude benchmark).
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
4 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: Complex: If price cap leads Russia to stop selling to the cappers and cannot fully reallocate to other buyers, there is a decrease in world supply and increase in the market.
price. If Russia sells to price cappers, then no obvious major effect on the remaining market price.
|
|||
Question A: The increasing share of income and wealth among the richest people in a number of advanced countries is giving significantly more political power to the wealthy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Agree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question B: The increasing share of income and wealth among the richest people in a number of advanced countries is having a significantly negative effect on intergenerational social mobility.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: in the previous question, we were talking about the 0.1% richest. In this one, more like the 10% richest.
|
|||
Question C: The increasing share of income and wealth among the richest people in a number of advanced countries is a major threat to capitalism.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question A: A windfall tax on the excess profits of large oil and gas companies – with the revenue rebated to households – would be an efficient way to provide temporary relief for the average household in European countries from rising energy costs.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: Because Europe is a net importer of energy, it cannot raise this way close to enough to subsidize consumers. Different in US
|
|||
Question B: Fiscal measures putting a cap on consumer energy prices would be a more appropriate immediate response to increased inflation in the euro area than raising interest rates.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Strongly Disagree |
8 |
|
Comment: This is a case where a larger fiscal deficit can make the job of monetary policy easier.
|
|||
Stablecoins that are not fully backed by either central bank reserves or government securities with minimal price volatility are inherently vulnerable to runs.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
10 |
Agree |
8 |
|
Comment: rarely is an answer so obvious
|
|||
High tariffs imposed by the European Union on imports of Russian natural gas would be an effective measure to reduce the flow of revenues to Russia while limiting disruption to supplies to Europe.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
8 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: Russia might decide to sell elsewhere, but at a lower price (Ural discount). May not decrease world supply much.
|
|||
Rather than using second-round runoffs to settle elections in which no candidate wins a first-round majority, the overall preferences of the electorate would be better reflected by using a single round with ranked-choice voting, in which voters are instructed to rank all of the candidates.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
6 |
Disagree |
5 |
|
Comment: it sounds right to this non expert, but one should never forget the Arrow impossibility theorem
|
|||
Question A:Rising energy prices suggest that the European Central Bank and the Federal Reserve will have to increase interest rates faster than they intended to before the invasion.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Uncertain |
8 |
|
Comment: problem more acute for fed than ecb. in europe, demand may be weak on its own, limiting inflation without the need for tighter money.
|
|||
Question B: Increased public spending by European countries to accommodate larger defense budgets, migration inflows and accelerated investment in alternative energy sources would be better financed mostly through taxes, rather than debt.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
8 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: on public finance grounds, some of it is for the future and can be financed by debt. And if demand is weak, deficit finance may be needed.
|
|||
Question C: Economic damage from the shock to global commodity markets will fall disproportionately hard on low- and middle-income countries.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
9 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: more dependence on food and energy.
|
|||
Question A:The fallout from the Russian invasion of Ukraine will be stagflationary in that it will noticeably reduce global growth and raise global inflation over the next year.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
5 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: I am reasonably confident about inflation, but less sure about output. Demand may be strong for other reasons.
|
|||
Question B: The economic and financial sanctions already implemented will lead to a deep recession in Russia.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
7 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question C: Targeting the Russian economy through a total ban on oil and gas imports carries a high risk of recession in European economies.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
5 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: by itself, yes. But there may be substantial additional public spending that may offset the contractionary effect.
|
|||
Question D: Weaponizing dollar finance is likely to lead to a significant shift away from the dollar as the dominant international currency.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
7 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
Comment: not sure about significant.
|
|||
Question A:High volatility in the prices of crypto assets such as Bitcoin, Dogecoin, and Ethereum largely reflects movements in investor sentiment rather than news about potential sources of fundamental value (such as possible applications, or use in illicit transactions).
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
7 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Given existing regulation of the financial system, as crypto assets grow in value and become more connected to the rest of the system, the fluctuations in their valuations will pose a serious risk to financial stability in advanced economies.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question C: Private unbacked crypto assets serve no important economic purpose.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
6 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A:Firms’ incentives to reduce costs by sourcing inputs and products abroad have caused many European industries to become more vulnerable to supply chain disruptions.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Private firms have inadequate incentives to make investments to reduce the risk that disruptions in the supply of imports will cause shortages and raise domestic prices.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
7 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: No strong externalities. One problem is that many have inconsistent plan Bs: relying on the same supplier, if something happens.
|
|||
Question C: Prioritisation of efficiency over resilience in global supply chains makes current disruptions likely to continue beyond 2022.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
7 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: Who says they are prioritizing efficiency over resilience?
|
|||
Question A:Given the centrality of semiconductors to the manufacturing of many products, securing reliable supplies should be a key strategic objective of EU and national policy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Europe’s small role in global semiconductor production is a direct result of insufficient private investment in high-tech innovation.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
5 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question C: Public support at EU and national level for investment along the value chain for semiconductors, including production, would be the most effective way to ensure security of supply.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: private firms have an incentive to do this on their own.
|
|||
Question A:Even without renewed Covid-19 restrictions, uncertainty about the health threat from the Omicron variant is likely to deliver a significant hit to economic activity from now through the first half of 2022.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: ``significant'' is too strong. Too early to say.
|
|||
Question B: If world vaccine supply continues to be limited, global social welfare would rise by more if those vaccines were made widely available across Africa (with support for effective delivery) rather than accelerating booster vaccinations in rich countries.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
4 |
Agree |
5 |
|
Comment: you are asking economists questions that they are not qualified to answer. They will nevertheless...
|
|||
Question C: Imposing travel bans on countries where new Covid-19 variants are discovered will make it less likely that countries will reveal new variants to the rest of the world.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
5 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: one of many potential effects. Many of the others work the other way.
|
|||
Question A: Voluntary national targets are unlikely to be an effective mechanism for achieving sharp reductions in greenhouse gas emissions.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: question is unclear. voluntary by firms (will not work), voluntary by governments (will work a bit better)?
|
|||
Question B: Agreement on a significant global price floor for all carbon emissions would be an effective step towards achieving sharp reductions in emissions.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question C: Green innovation in the private sector would be strongly stimulated by a substantial increase in public spending on R&D for climate change mitigation and adaptation.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
8 |
Agree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question A: The introduction of natural experiments to economic analysis of the labor market and related areas has led to a more precise understanding of cause and effect.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question B: The ‘credibility revolution’ in empirical economics has improved our understanding of a number of public policy issues, including education, immigration and the minimum wage.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question C: In pursuit of credible research designs, researchers often seek good answers instead of good questions.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
7 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: The initial phase was indeed good answers. But we have moved over time to good questions.
|
|||
Question A: A mandate for public companies to provide climate-related disclosures (such as their greenhouse gas emissions and carbon footprint) would provide financially material information that enables investors to make better decisions.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: better than nothing, but this will not change the world.
|
|||
Question B: A mandate for public companies to provide climate-related disclosures would induce them to reduce their climate impact significantly.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: same answer: it cannot do harm, but stronger measures (carbon price, or stronger) are absolutely needed.
|
|||
Question A: The current combination of US fiscal and monetary policy poses a serious risk of prolonged higher inflation.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
Comment: I object to ``serious''. I believe it is more likely to lead to a stronger reaction of the Fed than currently assumed, and higher rates.
|
|||
Question B: Current EU and national fiscal policy plans are likely to leave European output below potential a year from now.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
8 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
Comment: probably, based on existing plans. But a number of countries are likely to do more if it looks like it is needed.
|
|||
Question A:The introduction of even small trade frictions between neighboring countries can result in significant economic damage, particularly to smaller exporting firms.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
1 |
Agree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question B: A national economic boom based on natural resources is likely to harm other sectors of the economy, particularly manufacturing firms.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question A: A global minimum corporate tax rate would limit the benefits to companies of shifting profits to low-tax jurisdictions without biasing where they invest.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: An international tax system in which the major advanced economies set a minimum rate on corporate income is achievable.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question C: A global corporate tax system that is based on the location of final consumers would be more efficient than one based on the location of corporate headquarters and production facilities.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
8 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Under a fixed exchange rate and fully liberalized capital flows, a country loses domestic control of monetary policy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question B: For emerging and developing economies open to the world capital market, a flexible exchange rate confers little advantage over a pegged exchange rate in terms of economic stability.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
9 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
Comment: if combined with restrictions on capital flows
|
|||
Question C: The key feature making the US a more natural optimum currency area than the euro area is higher labor mobility.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Disagree |
8 |
|
Comment: fiscal union not far behind
|
|||
Question A: Reliable Covid-19 vaccines will reach developing countries more quickly if the rich countries pay the pharmaceutical companies at prevailing prices to manufacture and distribute the vaccines (or to license production and support licensees), rather than waiving patent protection.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
5 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: yes, but more expensive for govts.
|
|||
Question B: The benefits to the US, Canada, Europe, Japan and other rich countries of paying for 12 billion doses of Covid vaccines at prevailing prices and providing them for free to the rest of the world exceed the costs that the rich countries would incur.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
6 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A: The Bank for International Settlements defines a central bank digital currency as follows: ‘In simple terms, a central bank digital currency (CBDC) would be a digital banknote. It could be used by individuals to pay businesses, shops or each other (a 'retail CBDC'), or between financial institutions to settle trades in financial markets (a ‘wholesale CBDC').For developed countries, a central bank digital currency that is available to the public at large would offer social benefits that exceed the associated costs or risks.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
8 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
Comment: Risk of disintermediation of the banking sector, difficult to avoid
|
|||
Question B: Central banks that do not introduce their own digital money risk losing the ability to conduct effective monetary policy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
8 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
Comment: I have never understood this argument. Either private currencies float, or they sell at par. Neither case makes m policy irrelevant.
|
|||
Question C: The introduction of a central bank digital currency is unlikely to have major effects on the economy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
Comment: I may miss the vision thing. It may improve plumbing. But to me, it seems like much ado about not much.
|
|||
Question A: Removing intellectual property protections on Covid-19 vaccines would substantially improve availability of the vaccines in developing countries.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
5 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: that does not make it right...
|
|||
Question B: Removing intellectual property protections on Covid-19 vaccines would have a negative impact on vaccine development efforts for future variants of SARS-CoV-2 or for the next pandemic.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
1 |
Agree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question C: Without an international agreement that facilitates vaccine trade, countries’ incentives to limit exports of vaccines and/or key production inputs are likely to prolong the adverse effects of the pandemic in advanced countries.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Allowing short selling of financial securities, such as stocks and government bonds, leads to prices that, on average, are closer to their fundamental values.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
5 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: the usual caveat. the danger of short squeezes.
|
|||
Question B: Requiring investors to disclose short positions in a stock at the equivalent threshold as they are required to do for long positions would result in significantly less short selling.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
5 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: it would make short squeezes easier, and thus short sellers more careful.
|
|||
Question C: Regulatory restrictions on short selling - such as no naked shorts, temporary bans in times of crisis - make it difficult for optimists and pessimists to have equal influence on asset prices.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
5 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: but the trade off may be worth it
|
|||
Question A: EU Covid-19 vaccination efforts are significantly behind those of Israel, Serbia, the UK and the US.Offering substantially higher prices per dose would have resulted in larger capacity investments by vaccine makers and accelerated distribution in Europe significantly.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
5 |
|
Comment: Supply curves slope up... (but it does not necessarily mean that EU chose the wrong price. it may, it may not)
|
|||
Question B: In the current situation, paying for more production capacity would be better than offering higher prices for vaccines.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
5 |
|
Comment: again, holds as a matter of logic... if you want to affect production, subsidize production. Otherwise, money may leak elsewhere.
|
|||
Question C: If the EU started paying prices above 100 euros per dose, it would on net reduce the cost of the pandemic to the EU via more lives saved and shorter lockdowns.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
6 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: I do not know what the right price is...
|
|||
Question A: Policies that aim to reduce obesity by increasing incentives for physical activity would be more welfare-improving than policies that increase the financial costs of consuming calories.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
No Opinion |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: A ban on advertising junk foods (those that are high in sugar, salt and fat) would be an effective policy to reduce child obesity.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
No Opinion |
Agree |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C: Setting targets for schools to reduce obesity (e.g. by diverting financial resources to improve school meals or add cookery to the curriculum) would reduce social welfare because schools in deprived areas, where obesity is higher, are already struggling to deliver the core curriculum.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
No Opinion |
Disagree |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: The current US federal minimum wage is $7.25 per hour. States can choose whether to have a higher minimum - and many do.
A federal minimum wage of $15 per hour would lower employment for low-wage workers in many states.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
5 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: In some states, this would be a very large change. potentially sufficient large to trigger employment cuts.
|
|||
Question B: A federal minimum wage that is pegged to state and/or local conditions such as the cost of living would be preferable to the current arrangements that give states a role in setting the policy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: Adjustment for the cost of living is simply more fair. .
|
|||
Question A: The UK economy is likely to be at least several percentage points smaller in 2030 than it would have been if the country had remained in the European Union.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
4 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: The aggregate economy of the 27 countries still in the EU is likely to be at least several percentage points smaller in 2030 than if the UK had not left.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
4 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: Decisions may be easier to take. EU>>UK
|
|||
Requiring Facebook to divest WhatsApp and Instagram is likely to make society better off.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
4 |
Agree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Our understanding of labor productivity has been much enhanced by accounting for monetary and promotion-based incentives within firms and related selection effects.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Large salaries for senior business executives are less a reflection of an individual’s current contribution to a firm’s overall performance than a ‘prize’ for those who put in the effort to achieve one of the top positions.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: A wealth tax would be an effective way to reduce inequality.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: A wealth tax in a form discussed in the UK (where individuals could be taxed a percentage of their net worth over £750,000, excluding any personal pension savings and their main home) would be an effective way to improve public finances after the Covid-19 crisis.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question C: A public policy goal that could be accomplished with a well-enforced wealth tax could be accomplished at lower cost with modifications to existing taxes, such as income tax, capital gains tax, inheritance tax and property tax.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
8 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: not sure about the ``lower cost'' part. there are equivalence theorems, and then it depends on implementation problems.
|
|||
Question A: Google's dominance of the market for internet search arose mainly from a combination of economies of scale and a quality algorithm.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
4 |
Agree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question B: In light of Google’s dominance, its current operating practices could have a substantial negative effect on social welfare in the long run.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
5 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question C: The nature of the market dominance of technology giants in the digital economy warrants either the imposition of some kind of regulation or a fundamental change in antitrust policy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
5 |
Agree |
6 |
|
|
|||
The practical application of auction theory to the licensing of rights to use public assets like radiospectrum and other natural resources has generated substantially higher government revenues and better allocative efficiency worldwide than would have happened under previous arrangements.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Strong competition from foreign producers is likely to encourage greater private sector expenditure on research and development in the home market.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
No Opinion |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: The ECB should aim to achieve an inflation rate that averages 2% over time.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
8 |
Uncertain |
8 |
|
Comment: it all comes to the definition of ``average''. If fuzzy, may be counterproductive
|
|||
Question B:The ECB should take account of the environmental implications of its policy decisions.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
8 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
Comment: ``take into account'' is again ambiguous. It should know about it but its standard mandate has priority.
|
|||
Question C: The objectives set for the ECB by Treaty should make maximum sustainable employment of equal importance as price stability.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
Comment: minimizing the output gap is more important than minimizing distance of inflation to target. Fortunately, they largely coincide.
|
|||
Question A: Right now, the central focus of fiscal policy should be on temporary measures to provide protection and promote rapid economic recovery rather than trying to advance other objectives, such as reducing debt, tackling climate change or addressing inequality.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Agree |
8 |
|
Comment: Essential to focus on reducing bankruptcies and reducing unemployment. Using the appropriate tools.
|
|||
Question B: Cutting taxes on firms (or delaying tax collection) will allow more of them to survive and be more effective than public spending for triggering a rapid economic recovery.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: Helping viable but insolvent firms is a priority, essential for the short run, essential for the long run
|
|||
Question C: European recovery fund disbursements to crisis-hit countries should be primarily in the form of grants rather than loans.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
9 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: even if loans, mutualisation is useful. grants, if allocated efficiently across countries, would be even better
|
|||
Question D: European recovery fund disbursements to crisis-hit countries should not be made on condition of commitments to reform by recipients.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
8 |
Disagree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Given the social and regulatory pressures to keep prices down for drugs and vaccines to treat Covid-19, the financial incentives for pharmaceutical companies to invest in such products are below the value of the investment to society.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
4 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: Not sure this is the main factor.
|
|||
Question B: Government commitments to pay developers and manufacturers above average costs for an effective vaccine or drug treatments for Covid-19 would accelerate production.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
4 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: but again, high risk may be more of a constraint.
|
|||
Question C: Given the positive externalities from vaccination, an effective Covid-19 vaccine should have priority in public healthcare funding even in countries where other diseases cause more death and disability.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
4 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: as a matter of logic: what about other vaccines? as a matter of fact: should have high priority
|
|||
Question A: Political conflict plays a key role in shaping economic decisions, policies and outcomes.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Most European countries have larger social welfare systems than the United States in part because the latter is more heterogeneous by race and ethnicity.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
5 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Clearing the market for surgical face masks using prices is detrimental to the public good.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: Market clearing will lead the masks to go to those with the highest ability to pay, not the most need.
|
|||
Question B: Laws to prevent high prices for essential goods in short supply in a crisis would raise social welfare.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: This might decrease supply and be costly. But rationing may get the goods to those who have the most time and need.
|
|||
Question C: Governments should buy essential medical supplies at what would have been the market price and redistribute according to need rather than ability to pay.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: Clearly the best solution if it can be achieved. A small risk of cronysm in distribution, but worth taking
|
|||
Question A: Economic damage from the virus and lockdowns will ultimately fall disproportionately hard on low- and middle-income countries.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: They have to fight the virus, with a poor health system, low commodity prices, low remittances, capital outflows, and little fiscal space.
|
|||
Question B: A temporary standstill on sovereign debt payments by low- and middle-income countries to all official and private creditors to give those countries space to cover the immediate costs of the crisis would benefit advanced economies.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: it may well help AEs, by limiting the pandemic and the effects of defaults on the financial system. But this is not the reason to do it...
|
|||
Question C: Export restrictions on food and medical supplies, and other protectionist measures, are likely to cost lives and slow economic recovery in all countries.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: perverse effects have been shown clearly by Chad Bown in particular.
|
|||
Question A: Government support to private firms in the form of debt (either directly or with the help of public guarantees) is desirable, but risks leaving them with too much leverage to invest and grow in the future.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: if firm in trouble because of crisis loan, then chapter 11, or government as creditor changes loan to grant.
|
|||
Question B: Providing funds to viable businesses in the form of equity injections is a vital complement to debt support.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
8 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
Comment: ``vital'' is ambiguous. essential no. potentially useful for some: yes
|
|||
Question C: With the EU ban on state aid suspended, government capital injections should be provided via a newly created pan-European equity fund, rather than be left to national governments acting independently.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
8 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
Comment: again ``should'' is too strong. Risk sharing, in this form or any other, is highly desirable, but not absolutely required.
|
|||
Question A:Even with the support policies implemented by European governments in response to the crisis, low-income workers will suffer a relatively bigger hit to their incomes than those further up the distribution.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: poor more likely to be exposed to the virus if they work. more likely to lose income if laid off.
|
|||
Question B: With schools across Europe closed in the lockdown, existing gaps in access to quality education between high- and low-income households will be exacerbated.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Agree |
8 |
|
Comment: obvious differences in access to net, in ability of the family to help study
|
|||
Question C: Combating the effects of the pandemic on inequality should be a priority for policy interventions.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: The priority should be to fight the pandemic, not inequality. But, given that, anything that can be done to fight inequality is desirable.
|
|||
Question A: Severe lockdowns – including closing non-essential businesses and strict limitations on people’s movement – are likely to be better for the economy in the medium term than less aggressive measures.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Agree |
8 |
|
Comment: the conclusion of most of the models I have looked at.
|
|||
Question B: While national governments have responded to the crisis with substantial economic policy measures, a joint euro area fiscal response is still highly desirable.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
9 |
Strongly Agree |
8 |
|
Comment: desirable yes, highly perhaps not. can go a long way with just domestic fiscal policies
|
|||
Question C: Given the willingness of the European Central Bank to buy sovereign bonds, including Italian bonds, without limits, there is no need for ‘coronabonds’.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
9 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
Comment: Too strong: can do without bonds but with ecb commitment. more peace of mind with corona bonds
|
|||
Question A: Even if the mortality of COVID-19 proves to be limited (similar to the number of flu deaths in a regular season), it is likely to cause a major recession.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: The economic effects of COVID-19 coming from reduced spending will be larger than those coming from disruptions to supply chains and illness-related workforce reductions.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: the main effect may come from the restrictions needed to contain the epidemic.
|
|||
Question C: The economic policy institutions of the Eurozone are well equipped to ameliorate the potential economic damage from COVID-19.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
9 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
Comment: not without a change in fiscal attitudes and rules---which may come, under pressure
|
|||
Question A: Germany's current account surplus is undesirable even from a purely German viewpoint: the country would be better off if, for example, it ran a smaller primary surplus, in turn leading to a smaller current account surplus.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: Running a smaller primary surplus, so increasing demand and output would likely lead to a real appreciation and an increase in real income.
|
|||
Question B: The Eurozone would be in better shape if fiscal policy were more expansionary, which would allow monetary policy to be slightly less so.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: I believe that there is still a negative output gap in the euro zone, and m policy cannot help much.
|
|||
Question C: If there is a recession in the Eurozone, it will be essential to have a coordinated fiscal expansion.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
9 |
Agree |
8 |
|
Comment: fiscal expansion yes. Coordinated: better, but not of the essence.
|
|||
Question A: The European Union goal of reaching net zero emissions of greenhouse gases by 2050 will be a major drag on economic growth.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
7 |
Disagree |
5 |
|
Comment: Carbon taxes or caps are likely to lead to stranded assets, but alsohigh investment in new technologies. May come with higher tfp as well.
|
|||
Question B: Carbon taxes are a better way to implement climate policy than cap-and-trade.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
7 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: Weitzman discussion of prices versus quantities. Cap and trade more manipulable, but achieving given quantity for sure may be needed.
|
|||
Question C: A carbon border tax targeting imports from non-EU countries with less strict climate policies is likely to harm developing economies.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
5 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: Afraid that this may be right. May justify helping them through other channels.
|
|||
Question A: Following the UK election result, the certainty that the country is going to leave the European Union will provide a substantial short-term boost to the UK economy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
8 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
Comment: Two effects. The certainty of Brexit: bad. The removal of the uncertainty and option value: good. (+ election of a tory: good for business)
|
|||
Question B: Given that the transition period currently expires at the end of 2020, there is still a considerable risk that the UK will leave the European Union without a trade agreement.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question C: Leaving the European Union without a trade agreement would have a large negative impact on the UK economy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: likely adverse, size uncertain, and showing up slowly over time
|
|||
Question A: Under current policies on climate change, the associated physical risks (such as those arising from total seasonal rainfall and sea level changes, and increased frequency, severity, and correlation of extreme weather events) will be at most a very small factor in monetary policy decisions over the next decade.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: strange question... If there is a major global warming catastrophe, then I suspect this will affect all policies, monetary, fiscal, etc.
|
|||
Question B: The physical risks associated with climate change under current policies are likely to threaten financial stability over the next decade.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
8 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Europeans would benefit more from an extra €1 billion of public R&D spent through existing (public) channels than from an extra €1 billion of private R&D spent through existing (private) channels, all else equal.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
No Opinion |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Europeans would benefit more from an extra €1 billion of public medical research spent through existing (public) channels than from an extra €1 billion of private medical research spent through existing (private) channels, all else equal.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
No Opinion |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Randomized control trials are a valuable tool for answering some long unsettled questions in development economics research.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Randomized control trials are a valuable tool for making significant progress in poverty reduction.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
7 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Having companies run to maximize shareholder value creates significant negative externalities for workers and communities.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
10 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
Comment: Not necessarily. Depends on distortions in the market and in the economy as a whole.
|
|||
Question B: Appropriately managed corporations could create significantly greater value than they currently do for a range of stakeholders – including workers, suppliers, customers and community members – with small impacts on shareholder value.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
9 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: there are probably such cases. In general, it is primarily the job of the government to put in place the right regulations.
|
|||
Question C:Effective mechanisms for boards of directors to ensure that CEOs act in ways that balance the interests of all stakeholders would be straightforward to introduce.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
8 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
Comment: I believe in more representation of workers on the board, primarily for information and trust reasons.
|
|||
Question A:Rising inequality is straining the health of liberal democracy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
10 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: Based on my reading of the research, not the only reason, but, in most countries, the main one.
|
|||
Question B: Enacting more redistributive expenditures and policies would be likely to limit the rise of populism in Europe.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
10 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question C: European governments should allocate more resources to policies that would be likely to limit the rise of populism in Europe, even if it means higher public debt or lower public spending in other areas.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: This fits with my view that, in many countries, a more accommodating fiscal policy is needed on other grounds at this juncture
|
|||
Question A:At this point, there is little that the European Central Bank can do to increase or maintain output in the Eurozone.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
9 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
Comment: The ECB can buy large quantities, but with little effect on prices. (so long as it keeps the capital key, and it does not buy exotic assets)
|
|||
Question B: When the economy is operating below its potential, larger fiscal deficits are likely to increase demand and output.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: Unless utterly irresponsible, in which case adverse effects may dominate
|
|||
Question C: When the economy is operating below its potential and monetary policy is at the effective lower bound, fiscal policy should prioritize increasing output over decreasing public debt.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
Comment: costs of debt small. (output) benefits of deficits large
|
|||
Question A:Selecting candidates for membership of the ECB Executive Board based primarily on nationality ahead of competence is likely to have a negative effect on the quality of monetary policy in the Eurozone.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
9 |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Although the central bank can never be an entirely technocratic institution, the selection process for the ECB President and members of the Executive Board is significantly worsened by intergovernmental trade-offs involving appointments to other European institutions.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
9 |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
On bids for infrastructure projects, the average European would be better off if Europe’s governments favored European firms over Chinese firms (or firms from any other country with non-profit-related geopolitical strategies) — even if it means sometimes choosing a higher-cost bidder.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
1 |
Disagree |
5 |
|
Comment: I can see the case for it in some limited circumstances (major disruptions, economies of scale). I also can see the clear room for abuse.
|
|||
Question A: Breaking the “doom loop” — a negative spiral that can result when banks hold sovereign bonds and governments bail out banks — would increase the stability of European economies in the event of another financial crisis.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Agree |
8 |
|
Comment: i think investors often overestimate the budget risks, leading to a stronger doom loop than would be warranted
|
|||
Question B: Regulators should try to break the doom loop by assigning positive risk weights — in calculating banks’ capital requirements — to banks’ holdings of domestic and other Eurozone sovereign bonds.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question C: Breaking the doom loop would impose substantial costs on powerful political constituencies.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Uncertain |
8 |
|
Comment: governments with short horizons will not like it.
|
|||
Residents of big European cities would be better off, on balance, if governments did more to counter gentrification, for example by using rent and other housing subsidies, public housing investments, zoning regulations, or similar policies.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
9 |
Disagree |
5 |
|
Comment: On net, having cities with social and economic diversity is a good thing. But some residents will benefit, others will lose.
|
|||
Question A: A common European deposit insurance scheme, once fully implemented, would increase the stability of European economies in the event of another financial crisis.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question B: A common European deposit insurance scheme, once fully implemented, would increase the likelihood of another financial crisis in Europe.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Disagree |
9 |
Strongly Disagree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Overall, public spending on the arts in Europe creates benefits that exceed the deadweight loss caused by taxation to fund it.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
No Opinion |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
Comment: Entirely an empirical matter and I do not know the facts.
|
|||
Question B: Additional public spending on the arts in Europe would create incremental benefits that exceed the deadweight loss caused by taxation to fund it.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
No Opinion |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: The average European is better off if Europe’s competition authorities let firms merge into European champions in their sectors, even it weakens competition.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
6 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: If China and other countries use policies that create giant international firms, then the average European is better off if Europe's competition authorities let firms merge into European champions in their sectors, even it weakens competition.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
6 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
Comment: to me, the two questions are de facto the same. the answer must be uncertain, depending on specfics.
|
|||
Question A: Letting publicly traded European firms report earnings annually rather than quarterly would lead their executives to place more weight on long-term issues in their investments and other decisions.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
3 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question B: A switch from quarterly to annual earnings reports would, on net, benefit shareholders of European firms.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
3 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question A: To the extent that public corporations pursue social and environmental initiatives, they tend to achieve higher risk-adjusted (private) returns than otherwise similar corporations that pursue such initiatives less.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Disagree |
9 |
Disagree |
5 |
|
Comment: Hard to believe that adding constraints on portfolio choice leads to higher returns
|
|||
Question B: To the extent that Norway’s global government pension fund makes investments for social and environmental objectives — apart from investments that would bring the highest expected risk-adjusted returns — it improves the welfare of Norwegians.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
8 |
Agree |
5 |
|
Comment: If my knowledge is correct, the fund invests outside of Norway. So it may make the world a better place, but not necessarily Norway.
|
|||
Question A: The fiscal rules of the European Union should give more flexibility to member countries.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: the rules are rigid, but are broken with great regularity. There must be a better way.
|
|||
Question B: The Italian budget for 2019 that the European Commission rejected in October would have increased Italy’s risk of fiscal insolvency substantially.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
9 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: bad, but not the end of sustainability. https://piie.com/publications/policy-briefs/impact-italys-draft-budget-growth-and-fiscal-solvency
|
|||
Question C: If France runs a 2019 budget deficit of around 3.4% of GDP, as announced by President Macron’s government, France’s risk of fiscal insolvency will increase substantially.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Disagree |
9 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
Comment: with r less than g, debt dynamics are more favorable than they used to be. Some deficits, when needed, are ok.
|
|||
Question A: Capping the number of ride-sharing drivers as is being discussed in New York City, Chicago and London will make the average resident in that city worse off.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
Comment: This seems like a standard demand supply ec10 exercise, with no unusual features
|
|||
Question B:To achieve a given level of congestion, it would be better to use taxes for driving that vary based on the level of congestion, rather than limiting the number of ride-sharing vehicles.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
People who migrated to Europe between 2015 and 2018 are likely — over the next two decades — to contribute more in taxes paid than they receive in benefits and public services.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
2 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: Past may not be a good predictor. Depends on the composition, about which I know too little.
|
|||
Ideas are nonrival, so increasing returns to scale is an essential feature of technological change in a market economy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Voters overestimate the effect that current governments have on their economies’ concurrent economic performance.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: This is a no-brainer, backed by overwhelming evidence.
|
|||
Over the next decade, autonomous cars will raise average welfare in the EU by at least as much as smartphones have over the past decade.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
5 |
Disagree |
5 |
|
Comment: It may. it may not. Anybody who gives a more affirmative answer knows a lot more than me.
|
|||
Britain’s Labour party recently proposed giving the Bank of England a target of 3% annual labor productivity growth. Consider the following statement:Central banks cannot significantly increase productivity growth over a ten year horizon, except perhaps by promoting macroeconomic stability.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Agree |
8 |
|
Comment: why not ask for 10% productivity growth? (one footnote: hysteresis, if present, implies a slightly more aggressive monetary policy)
|
|||
Question A: The European Commission has proposed new rules to ensure that “digital business activities are taxed in a fair and growth-friendly way in the EU”. Consider two statements regarding this proposal:An EU-wide 3% tax on revenue from digital activities would, on balance, be a good idea.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
5 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question B:If the EU decides to tax digital service providers, it would be better — given the difficulties of measuring and verifying digital activity — to tax them on the revenue, rather than the profits, that they generate locally.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
5 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: The issue (both legal, and technical) is whether it can be done for digital companies and not for others.
|
|||
The European Union often uses its antitrust powers to protect EU-based firms from international competition, rather than to promote greater competition in European markets.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
3 |
Strongly Disagree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Trade with China makes most Europeans better off because, among other advantages, they can buy goods that are made or assembled more cheaply in China.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
8 |
Agree |
8 |
|
Comment: People as consumers win. People as workers may lose.
|
|||
Question B: Some Europeans who work in the production of competing goods, such as clothing and furniture, are made worse off by trade with China.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
9 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: indeed, some workers will lose their jobs. Some will find better ones, some will have a tougher time.
|
|||
Question C: If the EU followed the new US steel tariffs by imposing similar EU tariffs on steel from China, it would improve Europeans’ welfare.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
7 |
Strongly Disagree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Assuming it exits its third bailout program this summer without an immediate restructuring or other debt relief, Greece is unlikely to default on its sovereign debt in the coming decade.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Disagree |
8 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: If they have to pay market rates for new lending, it is very difficult to see how they will be able to repay.
|
|||
Question B: Greece would be better off if it had decided to exit the euro between 2011 and 2015.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
Comment: They would have needed help from others, but they would have been able to improve competitiveness much faster, and get growth going earlier
|
|||
Question C: If Greece had defaulted on (or restructured) its private debt in 2010, while also staying within the euro, that combination would have been better for Greece than either exiting the euro or proceeding as it has actually done.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
10 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: I argued that at the time.
|
|||
Question A: Bitcoins are more similar to gold than they are to currency.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Bitcoins are more similar to gold than they are to Dutch tulips in the 1630s.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
9 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
Comment: Like bitcoin, the two assets have some intrinsic value. Much of their price however reflects a bubble. A draw
|
|||
The US spends roughly 17% of GDP on healthcare, according to the OECD; most European countries spend less than 12% of GDP.
Higher quality-adjusted US healthcare prices contribute relatively more to the extra US spending than does the combination of higher quantity and quality of US care (interpreting quantity and quality to reflect both greater American healthcare needs due to underlying population health and the delivery of more or better healthcare services to Americans).
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
8 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: Example: Income of US doctors many times income of European doctors, with no evidence of difference in quality.
|
|||
Over the past two years, all else equal, the appeal of the US as a destination for immigrants has changed in ways that will likely decrease innovation in the US economy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
4 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A:Holding other policies fixed, the average European would be better off if every European country taxed corporate profits at a rate of 20% (based as closely as possible on a common definition of profits).
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
Comment: sure of the answer if ``at a common rate''. Not sure about the 20%, if different from current mean
|
|||
Question B: If other policies were held fixed and every European country taxed corporate profits at a common rate of 20%, then reducing that common rate substantially below 20% would make the average European better off.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Strongly Disagree |
6 |
|
Comment: if by average, we mean ``mean''. Distribution effects between capital and labor income might have adverse implications.
|
|||
Question A: All else equal, if corporations throughout Europe set quotas for a minimum number of women board members, the shareholder value of European companies would increase.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
3 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: Different perspectives are typically useful. Whether there is a sufficiently large pool of qualified women today is not obvious.
|
|||
Question B: Taking into account the likely effects on investments in human capital by men and women, setting quotas throughout Europe for a minimum number of women board members would generate substantial net benefits for Europeans.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
4 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Subsidizing renewable energy sources is better than taxing fossil fuels, assuming the subsidy or tax would be set at levels that would reduce carbon emissions by an equivalent amount.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
8 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
Comment: First pass: Fight a distortion, don't create a second one.
|
|||
Question B: Germany’s solar-energy subsidies to date have produced net social benefits for Germany.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
3 |
Disagree |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question C: Solar-energy subsidies to date in Germany and other countries have produced net social benefits for the world.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
3 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|||
Insights from psychology about individual behavior – examples of which include limited rationality, low self-control, or a taste for fairness – predict several important types of observed market outcomes that fully-rational economic models do not.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
10 |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
The influx of refugees into Germany beginning in the summer of 2015 will generate net economic benefits for German citizens over the succeeding decade.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
6 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: it very much depends on the degree to which the refugees eventually become integrated and productive. Not clear at this point.
|
|||
Question A: Holding labor market institutions and job training fixed, rising use of robots and artificial intelligence is likely to increase substantially the number of workers in advanced countries who are unemployed for long periods.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
6 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Rising use of robots and artificial intelligence in advanced countries is likely to create benefits large enough that they could be used to compensate those workers who are substantially negatively affected for their lost wages.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Consumers will be better off, on balance, if European cities treat firms that provide ride-sharing platforms (such as Uber) as substantively different from taxi firms, and thus not necessarily warranting the same regulation.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Assuming that taxi and ride-sharing companies were treated as substantively similar — including requirements that they operate on an equal footing regarding safety, insurance and taxation — letting ride-sharing services compete without restrictions on prices or routes would raise consumer welfare.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question C: Regardless of how ride-sharing services are treated, existing regulations for traditional taxi firms in many European cities harm consumers by limiting competition.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
1 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Revising France’s labor market policies — by reducing employment protection, decentralizing labor negotiations to the firm level, and making training programs more accessible and responsive to labor demands — would, all else equal, increase productivity in France’s economy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: those reforms are the right ones and should be implemented. Based on past empirical evidence, they should work. But one can never be sure.
|
|||
Question B: Reducing employment protection would reduce the equilibrium unemployment rate in France.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
9 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: Such a reform changes the nature of unemployment (shorter duration, higher flows) for the better. Net effect on the rate is ambiguous.
|
|||
Question A: The ECB's asset purchases over the past two years have reduced the threat of deflation in the euro area as a whole.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: Hard to see how monetary expansion, in whatever form, would do nothing for activity or inflation. Cannot think of strong perverse effects
|
|||
Question B: If the economic outlook in the euro area becomes less favorable, then increasing the ECB's asset purchase program (in size or duration) would substantially increase the euro area's economic growth over the following five years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: one may disagree with ``strongly''. but it would work in the right direction.
|
|||
In general, absent any inside information, an equity investor can expect to do better by holding a well-diversified, low-fee, passive index fund than by holding a few stocks.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Strongly Agree |
9 |
|
Comment: This is a no brainer. The only qualification is that the diversified portfolio may not be exactly the market portfolio.
|
|||
Question A: Without changes in policy, a rising share of people who are over age 65 will exert a substantial downward influence on per capita real GDP in western European countries.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: The direct effect is nearly by construction. The indirect effects, on pay as you go, on fiscal balance, are well documented
|
|||
Question B: In European countries where the share of those over 65 is rising, there are net social benefits to adjusting retirement ages for state-financed (including pay-as-you-go) pension systems upwards, so that revised retirement ages better reflect longer life expectancies.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Agree |
8 |
|
Comment: increase in retirement age, given increase in life expectancy and state of health, seems the least painful way to adjust.
|
|||
Question A: All else equal, there are substantial advantages to having much of Europe’s human capital and infrastructure for international financial activity clustered in a single city, as they are at present in London.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: All else equal, Britain’s rules on hiring, firing and working hours are significantly more conducive to financial activity than those in other large European countries.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Setting the EU rules aside, and assuming it would take 2.5% of Italy’s GDP to recapitalize its banks, the Italian government would improve financial stability in Europe if it injected this amount of public funds into its banks.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: if italy's debt is sustainable at 130%, it is surely sustainable at 132.5% if the financial system is functioning better.
|
|||
Question B: If Italy were to inject public funds into its banks without imposing losses on at least some claimants, an important cost would be the effect on future incentives (economic or political) in Europe.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
9 |
Agree |
8 |
|
Comment: this is the old moral hazard argument. i believe it is relevant, but of marginal importance empirically.
|
|||
Question A: Because of the Brexit vote's outcome, the UK's real per-capita income level is likely to be lower a decade from now than it would have been otherwise.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Agree |
8 |
|
Comment: I do not see the benefits which compensate the loss of full access to the EU market.
|
|||
Question B: Because of the Brexit vote's outcome, the rest of the EU's real per-capita income level is likely to be lower a decade from now than it would have been otherwise.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
6 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: Again, loss of full access to UK market is a minus, although small. Political implications re EU construction can go one way or the other
|
|||
In general, using more congestion charges in crowded transportation networks — such as higher tolls during peak travel times in cities, and peak fees for airplane takeoff and landing slots — and using the proceeds to lower other taxes would make citizens on average better off.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
10 |
Strongly Agree |
8 |
|
Comment: no brainer for an economist, so long as redistribution implications taken care of.
|
|||
On the whole, the shift from state to private ownership of many industrial assets in central and eastern European countries after communism has increased productivity in those countries.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
10 |
Strongly Agree |
8 |
|
Comment: This is a no brainer.
|
|||
Question A: Freer movement of goods and services across borders within Europe has made the average western European citizen better off since the 1980s.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
8 |
Strongly Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Freer movement of goods and services across borders within Europe has made many low-skilled western European citizens worse off since the 1980s.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Giving tax incentives to specific firms to locate operations in a country typically generates domestic benefits that outweigh the costs to the country providing the incentives.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
9 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: it depends on the demand elasticity. There are cases where it is greater than one, but cases where it is less. ``typically'' is too strong
|
|||
Question B: Europe as a whole benefits when European cities or countries compete with each other by giving tax incentives to firms to locate operations in their jurisdictions.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
10 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
Comment: well known case of tax competition driving rates to zero. Zero rates are not optimal.
|
|||
Question A: Freer movement of people to live and work across borders within Europe has made the average western European citizen better off since the 1980s.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Freer movement of people to live and work across borders within Europe has made many low-skilled western European citizens worse off since the 1980s.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
|
|||