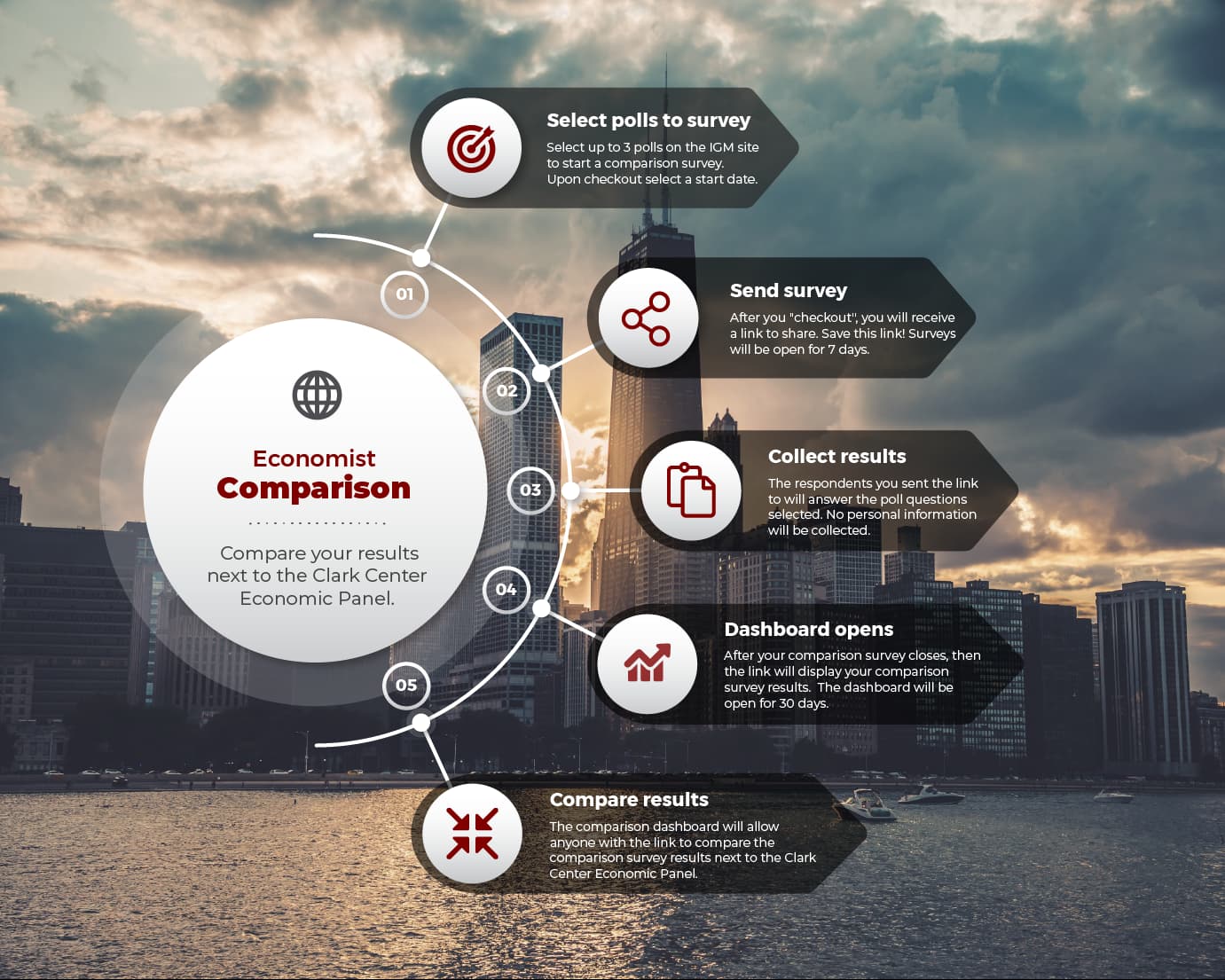
About
- The Moghadam Family Professor and Professor of Finance
- Fischer Black Prize (2021)
- Fellowship, Guggenheim Memorial Foundation (2019)
Voting History
Question A: The US dollar's status as the dominant reserve currency substantially raises its value.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: US-led policy interventions that discouraged central banks from holding US treasury securities would substantially diminish the dollar's reserve currency status.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
10 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: A reserve currency is based on fiscal capacity of the borrower and confidence of the holder in the safety of the payoff. Tampering with the payoffs (restrictions to sell or buy, default, inflation, FX depreciation) by the issuer will substantial lower its reputation.
-see background information here -see background information here -see background information here |
|||
Question C: US-led policy interventions that led to a sustained weakening in the dollar would substantially damage the US government's ability to finance its deficits.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
1 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: It depends on what investors believe the motivations of the borrower are, also on the existence of alternatives. If the depreciation is a side effect of other policies, ok. US went off Bretton Woods in 1973, but dollar remained central, probably due to lack of alternatives.
|
|||
Question A: A bipartisan bill to cap credit card interest rates at 10% has been introduced recently in the House and the Senate: https://ocasio-cortez.house.gov/media/press-releases/ocasio-cortez-luna-introduce-bill-cap-credit-card-interest-rates-10
Capping credit card interest rates at 10% would make most users measurably better off.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Disagree |
7 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Capping credit card interest rates at 10% would lead to a substantial reduction in access to credit for low-income borrowers.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
4 |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Giving the White House more direct influence over the decisions of the financial regulatory agencies would substantially improve financial stability.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
6 |
Strongly Disagree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Central banks' international reserves portfolios would have substantially lower risk if they were to hold a substantial portion of their reserves in crypto assets.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Disagree |
10 |
Strongly Disagree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question B: The US economy would benefit substantially by borrowing money to form a strategic crypto asset reserve fund.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Disagree |
10 |
Strongly Disagree |
8 |
|
Comment: This would strike me as one of the worst policy ideas ever.
|
|||
Question A: California's insurance industry regulator issued statements shortly before and shortly after the recent wildfires started (on December 30, 2024, and January 9, 2025):
https://www.insurance.ca.gov/0400-news/0100-press-releases/2024/release065-2024.cfm
https://www.insurance.ca.gov/0400-news/0100-press-releases/2025/release005-2025.cfm
In the face of growing wildfire risks, price caps on insurance premiums have substantially reduced the viability of private property insurance markets in California.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: A mandatory one-year moratorium on insurance non-renewals and cancellations would lead to a substantial longer-term reduction in the supply of private home insurance products and the number of households that are insured against catastrophic risk in areas of California affected by recent wildfires.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
A properly diversified 401k account should include private equity and private credit assets.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
3 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A: In general, absent any proprietary information, a retail equity investor cannot consistently make accurate predictions about whether the price of an individual stock will rise or fall on a given day.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Strongly Agree |
9 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: In general, absent any proprietary information, a retail equity investor can expect to do better by holding a well-diversified, low-fee, passive index fund than by holding a few stocks.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Strongly Agree |
9 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Establishing a sovereign wealth fund to invest in domestic infrastructure, emerging technologies, and/or strategic sectors would bring substantial benefits to the US economy over a ten-year horizon.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
5 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
Comment: Creating positive incentives in those areas would bring substantial benefits. For example via broad subsidies and taxes at sector level. Much less clear implementing this via sovereign wealth fund that buys equities in specific companies is the right policy implementation.
|
|||
Question B: For the US, establishing a sovereign wealth fund would be substantially better for citizens relative to reducing public debt burdens.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
5 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
Comment: At lower debt levels (say before the GFC) I would have argued for the US to issue safe debt and buy riskier assets. At present high level of debt, adding more government leverage and risk taking is a far less obvious policy.
|
|||
Question A: A bitcoin's value derives from the belief that others will want to use it, which implies that its purchasing power is likely to fluctuate over time to a degree that will limit its usefulness.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: A substantial source of the value of unbacked decentralized private cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, arises from their convenience for use in illegal activities.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
3 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: I have not seen detailed studies of how much value arises from this feature
|
|||
Question C: A properly diversified portfolio should include crypto assets.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
1 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
Comment: The market portfolio clearly includes these assets, since they exists and are traded
|
|||
Question A: The trend of consolidation in the US banking sector will lead to fewer, but more profitable, mega-banks with over $250 billion in assets dominating the market.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
2 |
Agree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question B: The current liquidity and capital regulations are inadequate to address run risks of banks in a digital era.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
1 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|||
It is appropriate advice for retail investors to tilt their portfolio away from the market portfolio towards factors that have been identified in the academic literature to earn positive abnormal returns relative to the Capital Asset Pricing Model.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
5 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
Comment: Especially if the "market portfolio" is in practice proxied by a broad equity index
|
|||
Question A:Stock markets around the world have seen an increasing concentration of trades in or near the closing auction. In the US, for example, about a third of all S&P 500 stock trades are now executed in the final ten minutes of the session, up from 27% in 2021.
The increased concentration of trading in the final minutes of the trading day has a measurably detrimental effect on market quality.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
1 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Strict indexing implemented with trading at the close to avoid tracking error creates a measurable performance drag that could be avoided with more flexible passive strategies.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
1 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Public companies that pursue social and environmental initiatives bear no measurable costs (in terms of lower profits) relative to similar companies that do not pursue such initiatives.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Disagree |
8 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
Comment: There are good or bad projects. If they pursue bad (low or negative NPV) projects purely to achieve a label on ESG the costs would be measurable. If they pursue good projects, which might include many with ESG orientation, then they would stand to gain.
|
|||
Question B: Public companies that pursue social and environmental initiatives benefit from a measurably lower cost of capital than similar companies that do not pursue such initiatives.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
5 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
Comment: I have not seen super reliable evidence on this. Estimating the cost of capital is notoriously difficult. Also the "benefits" might have been transitory from a moment when investors paid more attention to ESG labels.
|
|||
Question C: There are substantial social benefits when managers of public companies make choices that account for the impact of their decisions on customers, employees, and community members beyond the effects on shareholders.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: There are many externalities (pecuniary, demand, environmental, national security). It is often the role of the government to make managers (and other actors) internalize the externalities (regulation, tariffs, etc...)
|
|||
Question A: The lower willingness of private firms to go public, combined with the increased number of publicly traded firms being taken private over the last 25 years, is measurably net negative for economic growth.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: All else equal, reducing regulatory barriers (including reporting requirements such as Sarbanes Oxley 404) to public listing would substantially increase the share of publicly traded firms in the economy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C: The lack of transparency about unlisted private firms' financial performance substantially hinders the efficiency of the allocation of capital.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Letting publicly traded firms report earnings annually rather than quarterly would lead their executives to place more weight on long-term issues in their investments and other decisions.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
1 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: A switch from quarterly to annual earnings reports would, on net, benefit shareholders.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
4 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A: It seems likely that Japanese authorities intervened in the foreign exchange market recently to prop up the yen – see, for example: https://www.ft.com/content/455784ec-0465-46ee-8c73-fc5ce3e31c37. In such circumstances, intervention refers to purchases or sales of domestic or foreign currency without changing the monetary policy stance.
Large-scale intervention by public authorities in currency markets can move exchange rates substantially.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: Intervention has an impact via financial frictions on exchange rate markets. The more constrained the risk bearing capacity of the private market, the more intervention (for given size) moves the exchange rate
-see background information here -see background information here -see background information here |
|||
Question B: The effectiveness of foreign exchange interventions can last beyond one month.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
4 |
Disagree |
5 |
|
Comment: Clean empirical evidence is hard to find. Intervention is endogenous and so far we do not have papers credibly identifying the effects. My judgement comes from combining theory and existing evidence, so uncertainty is high, but on balance more positive than negative on effects.
|
|||
Retail investors account for a large share of global wealth, but a small share in private equity holdings. (see link: https://bain.com/insights/why-private-equity-is-targeting-individual-investors-global-private-equity-report-2023/)
A reduction in the barriers to all retail investors investing in private equity funds - notably regulatory restrictions on investor wealth/income and on liquidity - would substantially improve household welfare.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
2 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
Comment: On the margin, more participation could be good (as in risky assets in general), but one worries about investors getting into illiquid unsuitable products for their level of financial sophistication
|
|||
Regulator Probes BlackRock and Vanguard Over Huge Stakes in U.S. Banks – The WSJ reports that ‘The FDIC is scrutinizing whether the index-fund giants are sticking to passive roles when it comes to their investments in U.S. banks.’
The exemption of passive asset managers from banking rules - such as needing permission when they acquire shares above the 10% threshold - generates measurable risks to the accomplishment of the FDIC's mission.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Allowing short selling of financial securities, such as stocks and government bonds, leads to prices that, on average, are closer to their fundamental values.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
7 |
Agree |
8 |
|
Comment: While it is possible that enhanced speculative activity might cause distortions (especially in the short run and during a crisis), overall the first order effect is to get closer to fundamentals on average
|
|||
Question B: When short sellers start to establish substantial short positions in a stock, the stock is likely to have been overvalued.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
4 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: This variation, especially at high frequency might be more about speculation. So much would depend on the frequency
|
|||
Question C: Requiring investors to disclose short positions in a stock at the equivalent threshold as they are required to do for long positions would improve the informativeness of stock prices.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: I think the shorts should be disclosed as much as the long positions
|
|||
With some measures of concentration by market capitalization within broad US stock market indices at an all-time high, investors seeking a well-diversified passive equity portfolio should consider alternatives to market-cap-weighted indices.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
4 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
Comment: The market portfolio is what it is. More or less concentrated. So unless the indexes are not representative of the true market portfolio, why deviate? There is also a difference between partial equilibrium and general equilibrium...we cant all deviate the same way and still clear
|
|||
Tesla shareholders are likely to benefit substantially from the decision by the Delaware Court of Chancery to void Elon Musk's $56 billion remuneration package.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
No Opinion |
Disagree |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
On 10 January 2024, the SEC approved spot Bitcoin exchange-traded products:
https://www.sec.gov/news/statement/gensler-statement-spot-bitcoin-011023\
The SEC's approval of spot Bitcoin exchange-traded products makes investors overall measurably better off.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
2 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
|
|||
The Biden Administration's recommendation to lower the real discount rate used in the cost and benefit analysis of federal regulations to 2 percent (from the current levels of 3 or 7 percent) will substantially improve regulatory analysis.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
7 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: The previously higher rather were rather arbitrary. A lower rate might be appropriate, but what matters is the risk adjustment that depends on the risk and horizon of the project (e..g risk premia might be declining over the longer maturities)
-see background information here -see background information here |
|||
Question A: Harry Markowitz, the Nobel Prize-winning pioneer of modern portfolio theory, passed away earlier this year:
https://afajof.org/news/in-memoriam-harry-markowitz-past-president-of-the-american-finance-association-1927-2023/
Application of the principles of modern portfolio theory allows investors in practice to achieve substantial improvements in the risk-expected return trade-off relative to naive strategies such as equal-weighting that do not take account of return covariances.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Widespread adoption of modern portfolio theory by investors has substantially improved the efficiency of capital allocation in financial markets.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A: The Federal Reserve has begun quantitative tightening (QT) to reduce the size of its balance sheet. Fed holdings of Treasury securities have declined by $800 billion relative to the March 2020 peak. The Fed currently holds $4.9 trillion of Treasury securities, significantly larger than the $2.5 trillion holdings prior to the Covid pandemic.
A reduction in Fed holdings of Treasury securities measurably increases the interest rate on long-term U.S. Treasury bonds.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
8 |
Agree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question B: A reduction in Fed holdings of Treasury securities measurably increases volatility in the Treasury market.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
1 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: It depends on whether it flattens or steepens the demand curve, and also how it impacts flows from other participants. Not obvious what the outcome is.
|
|||
Question A: September 2023 was the 25th anniversary of the collapse of Long-Term Capital Management (LTCM). In response to LTCM's troubles, the Federal Reserve orchestrated a multi-billion dollar rescue package by a consortium of banks and it cut the Federal funds rate target by 75 basis points within six weeks.
The hedge fund sector's contribution to systemic risk is substantially lower today than at the time of LTCM.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
7 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: The hedge fund sector has expanded and is still largely unregulated. Much of it has moved offshore, Cayman Islands, or in onshore/offshore financial centers like Luxembourg and Ireland. Its levered positions recently contributed to US treasuries volatility and the UK LDI crisis.
|
|||
Question B: Financial market participants' expectation that the Fed will aggressively ease monetary policy in response to financial market dislocations is a substantial source of financial instability.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
7 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: It is a second best world response, but the Fed not easing or not intervening to calm markets would be worse. The more hazard effects this might induce can be addressed with ex-ante macro prudential policy.
|
|||
Question A: SEC Announcement: https://www.sec.gov/news/press-release/2023-155
The benefits of the new SEC rules on private funds - which require private funds to provide transparency to their investors regarding the fees and expenses and other terms of their relationship with private fund advisers and the performance of such private funds - substantially exceed their costs.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
No Opinion |
Disagree |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: The new SEC rules will have a substantially negative impact on the industry by stifling capital formation and reducing competition.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
No Opinion |
Disagree |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C: It is appropriate policy for the SEC to impose such rules on private funds even though the investors (limited partners) are sophisticated entities.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
No Opinion |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: New Money Market Fund (MMF) Rules: The SEC adopted amendments to the MMF rules, including a new mandatory liquidity fee for institutional prime and tax-exempt funds. The liquidity fee would trigger when daily net redemptions exceed five percent and when the costs associated with such redemptions are more than de minimus. https://www.sec.gov/news/press-release/2023-129
The new liquidity fee will substantially reduce the likelihood of runs on MMFs.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
1 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question B: The new liquidity fee will cause a substantial shift of assets under management from institutional prime and tax-exempt funds to government MMFs (which are exempt from the fees).
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
1 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A: The impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on working and shopping habits has not been fully priced into current private valuations of downtown commercial properties in major cities.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
1 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question B: A continued fall in commercial real estate valuations would trigger another round of banking panic.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
1 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Regulation that allows state pension funds to consider environmental, social, and governance factors in investment decisions only if these factors are material for risk and expected return would make retirees measurably worse off.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
5 |
Disagree |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Regulation that prevents state pension funds from considering environmental, social, and governance factors in investment decisions even if these factors are material for risk and expected return would make retirees measurably worse off.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
7 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: Being forced to ignore factors that materially affect risk-return tradeoff males investors worse off. Not specific to esg, but for most factors.
|
|||
Question A: Since maturity transformation is an inherent feature of commercial banks' business model, some duration mismatch between assets and liabilities is unavoidable.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
10 |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question B: For the purposes of capital regulation, banks should be required to mark their holdings of Treasury and Agency securities to market at all times (even though their loans are not marked to market).
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
3 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
Comment: In general I favor marking to market all assets for which there is a readily accessible price. Treasuries being one of them. For other assets, best effort on estimating changes in market value.
|
|||
Question A: Despite the empirical failures of the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) in explaining expected stock returns, a shareholder-value maximizing publicly-traded firm should still use the CAPM to calculate the cost of equity in capital budgeting.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
5 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: The equity risk premium that U.S. publicly traded firms should use in cost of equity calculations in April 2023 is above 6%.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
6 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Financial regulators in the US and Europe lack the tools and authority to deter runs on banks by uninsured depositors.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
4 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Not guaranteeing uninsured deposits at Silicon Valley Bank in full would have created substantial damage to the US economy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
2 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question C: Fully guaranteeing uninsured deposits at Silicon Valley Bank substantially increases banks’ incentives to engage in excessive risk-taking.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
4 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A: By issuing inflation-indexed bonds, and thereby providing a long-term real safe asset for pension funds and retirement savers, governments can make a substantial contribution to social welfare.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
1 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: In practice these bonds have tended to be illiquid and attract mixed interest. There are a number of measurement and indexing issues. The practical impact has been somewhat disappointing even if there are good theoretical reasons for this market to exist.
|
|||
Question B: Issuance of inflation-indexed bonds substantially helps government commit to a responsible fiscal and monetary policy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
6 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: Governments have many levers to tamper with the real payoff of debt (default, taxes, financial repression). Inflation is one of these levers. Inflation-indexed bonds reduce the ability to use this lever, but at the risk of the government simply using another lever more.
|
|||
Question A: Large-scale stock buybacks by public corporations provide short-term rewards for shareholders and senior executives at the expense of potentially higher-return corporate investments.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
2 |
Disagree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question B: The proposed higher tax on corporate stock buybacks (an increase from 1% to 4%) would generate substantial public revenues.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
1 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question C: The proposed higher tax on corporate stock buybacks would generate a substantial increase in corporate investment.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
1 |
Disagree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Missing payments on the US Treasury security obligations for several weeks would pose a substantial risk of a global financial crisis.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
2 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: It would certainly not be a positive event, but the details would matter. It mostly would introduce an "incompetence risk premium" into Treasuries by making it clear that the political system is now so dysfunctional that even the federal debt repayment can be used for bargaining
|
|||
Question B: The requirement to periodically increase the debt ceiling measurably reduces the long-run size of the debt.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Disagree |
8 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question A: The SEC’s proposed new rule for stock orders from individual investors is likely to be effective in giving those investors better prices on their trades on average.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
No Opinion |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: The new rule would improve the overall operation of the stock market.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
No Opinion |
Disagree |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Although the reported volatility of asset values in private markets (private equity, buyouts, and venture capital) is lower than that of comparable assets in public markets, their true volatility is broadly similar or greater.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
No Opinion |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
Comment: It seems plausible due to assets not being marked to market.
|
|||
Question B: Since the global financial crisis, the realized returns on private equities have measurably exceeded the returns on public equities.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
No Opinion |
Disagree |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: The collapse of a major crypto intermediary will have little impact on the wider economy and the stability of the traditional financial system.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
2 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: At the current scale and level of usage, crypto does not seem systematic enough to cause major issues to the wider financial system. But my level of uncertainty is high since I am not an expert on the issue and have not seen a detailed data analysis.
|
|||
Question B: The collapse of a major crypto intermediary suggests the need for the crypto asset class to be more tightly regulated.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
10 |
Agree |
8 |
|
Comment: I do not think it is the collapse per se (even under optimal regulation one might still want some collapses to occur), but the reasons for the collapse that point to the need for tighter regulation.
|
|||
The amount of passively invested funds has reached levels at which it has a measurable detrimental effect on market efficiency.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
3 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Research on the nature and impact of bank runs has made it possible to limit substantially the wider economic damage from financial crises.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
3 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: The research has certainly improved our understanding of these crises. Our management of the crises has improved...as for "substantially", I am not sure. Certainly better than how the Fed managed the great depression.
|
|||
Question B: Reforms of financial regulation since 2008 (and macroprudential policies in some countries) will not substantially reduce the probability of financial crises.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
No Opinion |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
|
Comment: The question is not answerable. It is asking for a quantitative assessment about "substantially reducing a probability" without defining substantially.
|
|||
Question A: The costs and risks associated with a sharp fall in the value of sterling outweigh any macroeconomic benefits for the UK of export stimulus due to a weaker currency.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: I think the costs of large and disorderly market moves can be large, especially if systemic financial institution get into trouble as a result. The benefit to the UK of a depreciation is hard to assess (the evidence is mixed in the literature) and probably significantly smaller.
|
|||
Question B: Concerns about government finances and debt sustainability can undermine the reserve currency status of a major currency.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
10 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: A loss of investor confidence in the fiscal commitment of a reserve country to maintaining the real value of its debt repayments is the core threat to the status of that currency. At the core, a reserve currency is a fiscal commitment to providing a safe asset.
-see background information here |
|||
Question A: The typical chief executive officer of a publicly traded corporation in the U.S. is paid more than his or her marginal contribution to the firm's value.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Mandating that U.S. publicly listed corporations must allow shareholders to cast a non-binding vote on executive compensation was a good idea.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
10 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Having companies run to maximize shareholder value creates significant negative externalities for workers and communities.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
10 |
Disagree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Appropriately managed corporations could create significantly greater value than they currently do for a range of stakeholders – including workers, suppliers, customers and community members – with negligible impacts on shareholder value.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Disagree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question C: Effective mechanisms for boards of directors to ensure that CEOs act in ways that balance the interests of all stakeholders would be straightforward to introduce.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
10 |
Disagree |
8 |
|
Comment: This is a complex problem theoretically, with in practice many political and practical implementation limitations. Not straightforward.
|
|||
Question A: A mandate for public companies to provide climate-related disclosures (such as their greenhouse gas emissions and carbon footprint) would provide financially material information that enables investors to make better decisions.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: A mandate for public companies to provide climate-related disclosures would provide material information that enables investors to make better decisions with regards to non-financial objectives (such as aiding portfolio choice based on ESG principles).
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question C: A mandate for public companies to provide climate-related disclosures would induce them to reduce their climate impact substantially.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
6 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: Unclear what the outcome would be. I also note that the previous questions only focused on whether a mandate would produce relevant information. They did not ask about the cost of the mandate and tradeoffs.
|
|||