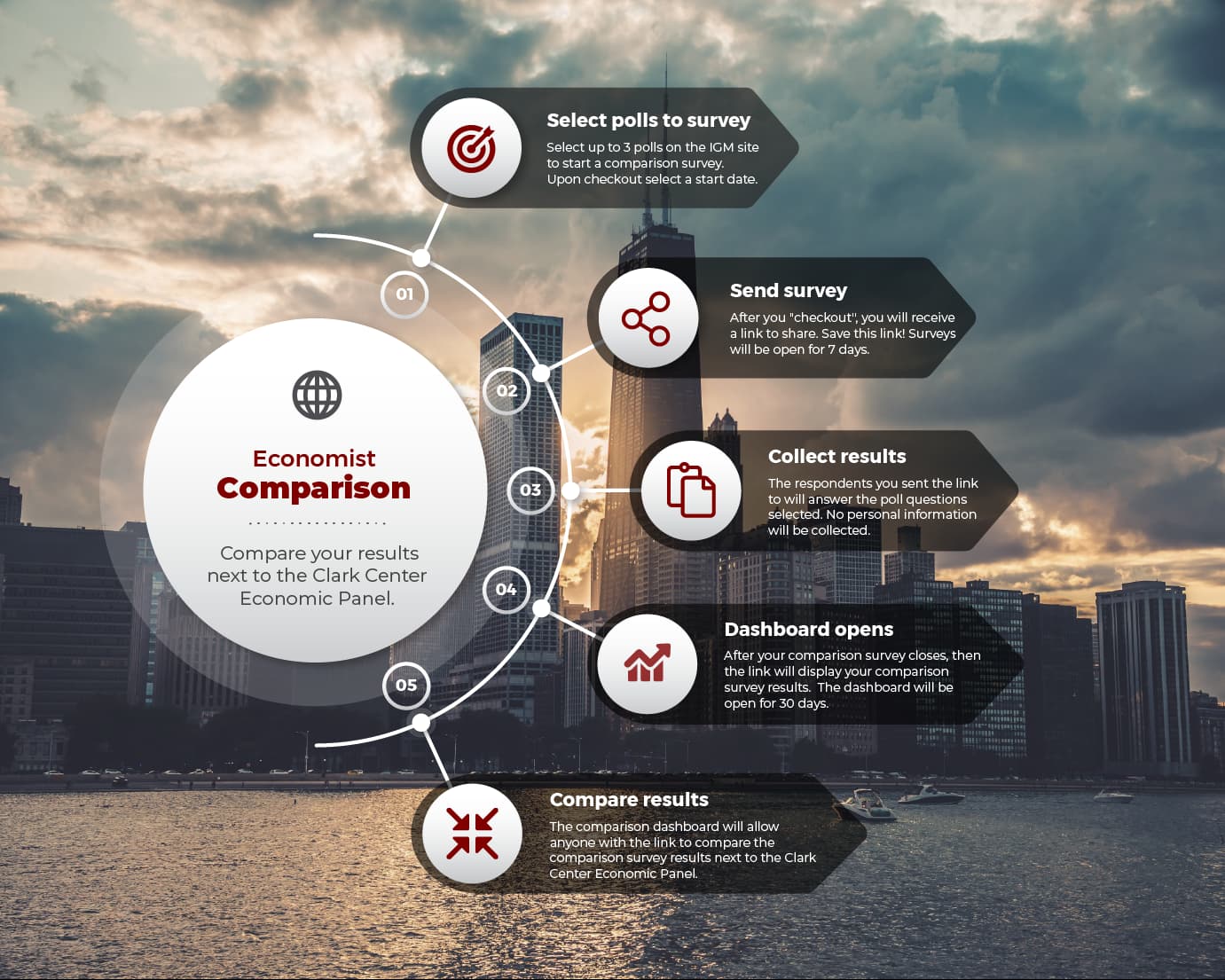
About
- Professor of Economics and Strategy
- Head of Economics, Knowledge and Industry, Board Member, Ciudadanos Party (Spain)
- Research Fellow, Center for Economic Policy Research (CEPR) and Co-Director of the CEPR Program in Industrial Organization (2007-11)
- Banco Herrero Prize (2007)
Voting History
Question A: The reductions in Western programs of development assistance will have no measurable effects on GDP growth in the recipient countries over the next five years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: The reductions in Western programs of development assistance will have substantially negative effects on the most vulnerable people in the recipient countries over the next five years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C: Development assistance motivated by the potential benefits for the donors in terms of prosperity and security is measurably more effective in promoting GDP growth in recipient countries than aid based on humanitarian or other moral principles.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Matching US import tariffs to the tariffs, value-added taxes and non-tariff barriers imposed on US goods by other countries would substantially reduce the US trade deficit.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: The threat of retaliation against the imposition of higher tariffs on a country’s exports substantially lowers the probability of a trade war.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C: In the event that the threat of retaliation does not deter the imposition of tariffs, the economies of countries subject to higher tariffs on their exports would be measurably better off by responding with targeted tariffs on imports from the first mover.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: The wave of immigration to Germany after 2015 (and up to the Russian invasion of Ukraine) has been a net positive for the country's economy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Immigration to EU countries has been a net positive for government finances, adding substantially more in tax revenues than the increased costs associated with integration of immigrants.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C: Given Europe's low and falling fertility rates (from seven million births per year in 1960 to four million today), maintaining its position as a world economic power will require increased immigration over the medium term.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Putting America First in International Environmental Agreements: https://www.whitehouse.gov/presidential-actions/2025/01/putting-america-first-in-international-environmental-agreements/
'In recent years, the United States has purported to join international agreements and initiatives that do not reflect our country's values or our contributions to the pursuit of economic and environmental objectives... The United States Ambassador to the United Nations shall immediately submit formal written notification of the United States' withdrawal from the Paris Agreement under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change.'
US withdrawal from the Paris climate agreement will deliver a measurable boost to the country's economic growth over the next four years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: US withdrawal from the Paris climate agreement will have a measurably negative impact on international progress on mitigation of global warming.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: A baseline US tariff of 10% on all European imported goods would have substantially damaging economic consequences for many countries in Europe.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
8 |
Agree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Rather than responding to threatened tariffs with retaliatory measures, unilaterally opening EU markets to US exports would deliver better outcomes for European industry.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
6 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: This is a transactional president. If he thinks he can dominate Europe, he will. ultimately, that will be worse for European industry.
|
|||
Question C: Disruptions to global supply chains from new tariffs and trade wars will lead to measurably slower global growth over the next five years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
6 |
Agree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question A: The likely need for increased European public investment in defense should come with substantial reallocations of public budgets at the national and EU levels.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
10 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: There is no free lunch: guns or butter.
|
|||
Question B: Greater use of joint EU-level procurement of military equipment and defense research/innovation would promote substantially enhanced capacity in Europe's defense industry.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
10 |
Agree |
5 |
|
Comment: Economies of scale and specialization are crucial. We already spend more than Russia, only together we can make it count.
|
|||
Question C: Increased defense spending would deliver a measurable boost to economic growth in Europe over the next five years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
1 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: There is going to be certainly a lot of idle capacity in industry. But whether 1% (max) extra) GDP on defense will meaningfully affect growth is unclear. I believe the constraints to growth are others (notably energy).
|
|||
On the basis of current climate policy commitments and potential technology and market responses, my current best estimate for global warming is that average global temperatures by 2100 will rise to no more than 2.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: A period of high inflation is substantially more electorally damaging to incumbent governments in advanced countries than a period of high unemployment.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Voters are more likely to punish incumbents for what they perceive as poor national economic performance than they are to reward incumbents for a good economy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: The institutions of society - such as constitutions, laws, judiciaries, and property rights - substantially shape economic decisions, policies, and outcomes.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Strongly Agree |
8 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: On average and over the long term, democracies deliver substantially better economic growth than other forms of government.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C: Countries where democracy and the rule of law are weakened are likely to experience measurable damage to their economic performance.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Current enforcement of competition policy in Europe is not working to promote innovation and growth.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Disagree |
7 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: The work of the Competition DG and Commissioner has been pro-market and pro-innovation. The problem has come from excessive regulation. Stopping within country telecom mergers is good, contrary to all lobbying messages of telcos.
|
|||
Question B: European Union bureaucracy and regulations are a substantial constraint on innovation in Europe.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: GDPR has been shown (see URL) to be reducing dynamism in several dimensions. The excessive fragmentation of the single market and double and triple regulatory layers (see e.g. banking) certainly reduce economies of scale and productivity.
-see background information here |
|||
Question C: The conduct of the dominant US tech companies in European markets (including lobbying and acquisition of start-ups and competitors) is a substantial constraint on innovation in Europe.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
6 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question A: In pursuing social and environmental initiatives, the average public company generates more benefits than costs in terms of profits.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: In pursuing social and environmental initiatives, public companies would benefit from a measurably lower cost of capital.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C: There are substantial social benefits when managers of public companies make choices that account for the impact of their decisions on customers, employees, and community members beyond the effects on shareholders.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: US antitrust investigations of the dominant firms in artificial intelligence are warranted by the need to foster competition and innovation in the technologies.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Seeking to slow the pace of artificial intelligence use and implementation would be a more effective means of assessing potential harms from the technologies than market deployment and ex post assessment.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
4 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: The proposed US tariffs on Chinese EVs would lead to measurably higher employment in the US automotive industry over the next five years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
6 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question B: The proposed US tariffs on Chinese EVs would measurably slow the adoption of green technology by consumers.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
1 |
Agree |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question C: Unless the EU matches the proposed US tariffs on Chinese EVs, there would be measurably lower employment in Europe's automotive industry over the next five years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
6 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Greater integration of national markets for financial services, energy and telecommunications would give a measurable boost to Europe’s GDP over the next ten years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: Energy market fragmentation will be increasingly costly given the seasonality of energy markets. Financial market integration will avoid the risks of doom loops, plus increased scale will increase financing for innovative ventures (which now are prone to leave for US).
|
|||
Question B: The potential benefits for GDP from loosening European merger rules to allow greater consolidation within the single market would outweigh the potential harm to consumers from weaker competition.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
6 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: I don't see any reason to losen merger rules. They are fine and adequately only concern mergers with a significant impact on the EU market.
|
|||
Question A:Creation of a more unified capital market in Europe - with a common pool of capital, a single rule book and a strengthened European Securities and Markets Authority, comparable to the US Securities and Exchange Commission – would lead to a substantial shift in the balance of companies listing their shares in the EU vis-a-vis the US.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Creation of a more unified capital market in Europe - with a common pool of capital, a single rule book and a strengthened European Securities and Markets Authority, comparable to the US Securities and Exchange Commission – would substantially increase the availability of funding for start-ups and growing companies across the EU.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: One crucial instance where harmonization would help is what happens when a company fail. Bankruptcy procedures are different across Europe and they mean that owning a share, a bond, providing a security to a counterparty means a different things in different countries.
|
|||
Question A: The European Union's AI Act was approved by the European Parliament in March 2024: https://artificialintelligenceact.eu/the-act/
The EU's legislation to regulate artificial intelligence is likely to put European technology firms at a substantial disadvantage to their competitors elsewhere in the world.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
7 |
Disagree |
5 |
|
Comment: The lAI act certainly increases compliance costs. This is a minus. But it also provides incentives for open source and transparency, which could facilitate catch up. The balance is probably negative.
-see background information here |
|||
Question B: By providing a clear set of rules, the EU's legislation on artificial intelligence is likely to enhance research and innovation by firms building the new technology.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
7 |
Disagree |
4 |
|
Comment: There is little question that, in areas defined as harmful, including e.g. cars and large LLMs (size is a measure of risk in the legislation for GenAI models) the regulatory and compliance burden is larger and hence research and innovation will decrease.
|
|||
Question A: Europe’s economic growth performance over the last 25 years has been measurably better than it would have been in the absence of the single currency.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: With euro area member states having given up their ability to carry out independent monetary policy, it is substantially more difficult for them to respond effectively to country-specific macroeconomic disturbances.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
8 |
|
|
|
|||
A legalized and carefully regulated market for cannabis would lead to measurably higher social welfare than a system of prohibition.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
8 |
Agree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question A: The economic and financial sanctions against Russia are substantially limiting its ability to wage war on Ukraine.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
5 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: Trade data from countries around the Caucasus suggest that, after a severe initial hit, Russia has successfully rewired it's economy for war.
|
|||
Question B: In the absence of continuing flows of Western economic aid, Ukraine's wartime economy will be substantially compromised.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
10 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: Ukraine is a significantly smaller country than Russia. This effort is unsustainable on its own
|
|||
Question A: A constitutional rule that limits the size of budget deficits that governments can run as a share of GDP is an effective way to impose discipline on a country’s public finances.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
6 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Germany’s debt brake is a substantial constraint on vital public investment in physical/digital infrastructure and the green transition.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
6 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: Investments do not need to be finances with debt
|
|||
Question A:The fundamental cause of Argentina’s high inflation is unfunded fiscal commitments that are being financed by the central bank.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
10 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Even if Argentina could marshal the resources to make a full switch to using US dollars for domestic transactions, it would substantially increase the volatility of Argentine GDP.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
5 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A: It is best for society if the management of publicly traded corporations only considers the impact of their decisions on customers, employees, and community members to the extent that these effects feedback to affect shareholder wealth.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
9 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question B: The typical chief executive officer of a publicly traded corporation is paid more than his or her marginal contribution to the firm's value.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
8 |
Uncertain |
6 |
Question A: By enabling women’s life choices about education, work and family, the contraceptive pill made a substantial contribution to closing gender gaps in the labor market for professionals.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Gender gaps in today’s labor market arise less from differences in educational and occupational choices than from the differential career impact of parenthood and social norms around men's and women’s roles in childrearing.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C: The gender gap in pay would be substantially reduced if firms had fewer incentives to offer disproportionate rewards to individuals who work long and/or inflexible hours.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: The EU's taxonomy for sustainable activities - a classification system that defines criteria for economic activities that are aligned with a net zero trajectory by 2050 and the broader environmental goals other than climate - is an effective way to steer greener investment and the energy transition by firms and financial institutions.
Details on the taxonomy are here:
https://finance.ec.europa.eu/sustainable-finance/tools-and-standards/eu-taxonomy-sustainable-activities_en
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
10 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: The EU taxonomy is a bit like the old Yahoo search engine: a set of categories and subcategories. It freezes a hugely changing reality at a moment in time. It will steer investment ,but I fear it will be too rigid and arbitrage ridden.
|
|||
Question B: Use of the EU taxonomy for sustainable activities is likely to stifle important innovations, including in green technology.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: Again, it has to do with the fact that what may appear to the legislator brown at some point may be able to become green in ways that the legislation did not envisage.
|
|||
Question C: On balance, use of the taxonomy in EU directives and regulation is likely to be net beneficial to European citizens.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
8 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: I think the EU needs to reconsider this approach. We have a very good alternative: a price system, the ETS together with CBAM, that allows us to tax Carbon. Private investment is much more likely to be efficiently incentivized by having to pay a price for CO2.
|
|||
Question A: Fiscal rules on budget deficits and public debt levels are an essential part of a sound fiscal framework.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Since the inception of the Stability and Growth Pact, budget deficits in Europe have been measurably lower, on average, than would have been the case without common budget rules.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C: Since the inception of the Stability and Growth Pact, the path of GDP growth in Europe has been measurably more stable than would have been the case without common budget rules.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Non-bank financial intermediaries pose a substantial threat to financial stability.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Regulating the leverage and liquidity of non-bank financial intermediaries would substantially improve financial stability.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C: Given current regulations, non-bank financial intermediaries should not have access to central bank support.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: A significant factor behind today’s inflation in Europe is dominant corporations in uncompetitive markets taking advantage of their market power to raise prices in order to increase their profit margins.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: A significant factor behind today’s inflation in some sectors of the European economy is dominant corporations in uncompetitive markets taking advantage of their market power to raise prices in order to increase their profit margins.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C: A significant factor behind today’s inflation in some sectors of the European economy (both competitive and concentrated) is distortions in the aggregate economy where supply does not meet demand.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: If countries could impose a ban on the use of ChatGPT and similar generative AI chatbot services that is technologically effective, they would experience a measurably negative impact on national innovation.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: This is a general purpose technology that has the potential to generate a wide range of innovations in many fields, as well as increasing labor productivity in knowledge-based occupations.
|
|||
Question B: Regardless of whether advances in AI spur productivity growth, they are likely to create deep challenges for society – in areas from labor markets to politics, and including disinformation, privacy, crime, and warfare – that will be difficult to anticipate, plan for, and contain.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
8 |
Agree |
6 |
|
Comment: The consequences for political discourse (fake news etc) as well as for labor markets zee most inmediate and almost certain, even without taking into account the larger concerns some experts in neural networks express
|
|||
Question A: Use of artificial intelligence over the next ten years will lead to a substantial increase in the growth rates of real per capita income in the US and Western Europe over the subsequent two decades.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Use of artificial intelligence over the next ten years will have a substantially bigger impact on the growth rates of real per capita income in the US and Western Europe over the subsequent two decades than the internet has had over the past two decades.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Preserving the financial viability of France's state pension system is better achieved by raising the effective retirement age than by raising contributions while working.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Preserving the financial viability of France's state pension system is better achieved by raising the effective retirement age than by reducing benefits once retired.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A:At this point, there is little that the European Central Bank can do to increase or maintain output in the Eurozone.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: When the economy is operating below its potential, larger fiscal deficits are likely to increase demand and output.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C: When the economy is operating below its potential and monetary policy is at the effective lower bound, fiscal policy should prioritize increasing output over decreasing public debt.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A:Selecting candidates for membership of the ECB Executive Board based primarily on nationality ahead of competence is likely to have a negative effect on the quality of monetary policy in the Eurozone.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
8 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Although the central bank can never be an entirely technocratic institution, the selection process for the ECB President and members of the Executive Board is significantly worsened by intergovernmental trade-offs involving appointments to other European institutions.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
8 |
|
|
|
|||
On bids for infrastructure projects, the average European would be better off if Europe’s governments favored European firms over Chinese firms (or firms from any other country with non-profit-related geopolitical strategies) — even if it means sometimes choosing a higher-cost bidder.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Breaking the “doom loop” — a negative spiral that can result when banks hold sovereign bonds and governments bail out banks — would increase the stability of European economies in the event of another financial crisis.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
8 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Regulators should try to break the doom loop by assigning positive risk weights — in calculating banks’ capital requirements — to banks’ holdings of domestic and other Eurozone sovereign bonds.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
8 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C: Breaking the doom loop would impose substantial costs on powerful political constituencies.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
8 |
|
|
|
|||
Residents of big European cities would be better off, on balance, if governments did more to counter gentrification, for example by using rent and other housing subsidies, public housing investments, zoning regulations, or similar policies.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: A common European deposit insurance scheme, once fully implemented, would increase the stability of European economies in the event of another financial crisis.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
8 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: A common European deposit insurance scheme, once fully implemented, would increase the likelihood of another financial crisis in Europe.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Strongly Disagree |
8 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Overall, public spending on the arts in Europe creates benefits that exceed the deadweight loss caused by taxation to fund it.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Additional public spending on the arts in Europe would create incremental benefits that exceed the deadweight loss caused by taxation to fund it.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: The average European is better off if Europe’s competition authorities let firms merge into European champions in their sectors, even it weakens competition.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: If China and other countries use policies that create giant international firms, then the average European is better off if Europe's competition authorities let firms merge into European champions in their sectors, even it weakens competition.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Letting publicly traded European firms report earnings annually rather than quarterly would lead their executives to place more weight on long-term issues in their investments and other decisions.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: A switch from quarterly to annual earnings reports would, on net, benefit shareholders of European firms.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: To the extent that public corporations pursue social and environmental initiatives, they tend to achieve higher risk-adjusted (private) returns than otherwise similar corporations that pursue such initiatives less.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: To the extent that Norway’s global government pension fund makes investments for social and environmental objectives — apart from investments that would bring the highest expected risk-adjusted returns — it improves the welfare of Norwegians.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: The fiscal rules of the European Union should give more flexibility to member countries.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: The Italian budget for 2019 that the European Commission rejected in October would have increased Italy’s risk of fiscal insolvency substantially.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C: If France runs a 2019 budget deficit of around 3.4% of GDP, as announced by President Macron’s government, France’s risk of fiscal insolvency will increase substantially.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Capping the number of ride-sharing drivers as is being discussed in New York City, Chicago and London will make the average resident in that city worse off.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B:To achieve a given level of congestion, it would be better to use taxes for driving that vary based on the level of congestion, rather than limiting the number of ride-sharing vehicles.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
8 |
|
|
|
|||
People who migrated to Europe between 2015 and 2018 are likely — over the next two decades — to contribute more in taxes paid than they receive in benefits and public services.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Ideas are nonrival, so increasing returns to scale is an essential feature of technological change in a market economy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Voters overestimate the effect that current governments have on their economies’ concurrent economic performance.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Over the next decade, autonomous cars will raise average welfare in the EU by at least as much as smartphones have over the past decade.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Britain’s Labour party recently proposed giving the Bank of England a target of 3% annual labor productivity growth. Consider the following statement:Central banks cannot significantly increase productivity growth over a ten year horizon, except perhaps by promoting macroeconomic stability.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
8 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: The European Commission has proposed new rules to ensure that “digital business activities are taxed in a fair and growth-friendly way in the EU”. Consider two statements regarding this proposal:An EU-wide 3% tax on revenue from digital activities would, on balance, be a good idea.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B:If the EU decides to tax digital service providers, it would be better — given the difficulties of measuring and verifying digital activity — to tax them on the revenue, rather than the profits, that they generate locally.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
The European Union often uses its antitrust powers to protect EU-based firms from international competition, rather than to promote greater competition in European markets.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Strongly Disagree |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Trade with China makes most Europeans better off because, among other advantages, they can buy goods that are made or assembled more cheaply in China.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Some Europeans who work in the production of competing goods, such as clothing and furniture, are made worse off by trade with China.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
1 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question C: If the EU followed the new US steel tariffs by imposing similar EU tariffs on steel from China, it would improve Europeans’ welfare.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Disagree |
9 |
Strongly Disagree |
7 |
|
Comment: (1) China retaliation and inevitable escalation
(2) destroying rule based-trade, where disputes are settled by WTO norms and "courts"
|
|||
Question A: Assuming it exits its third bailout program this summer without an immediate restructuring or other debt relief, Greece is unlikely to default on its sovereign debt in the coming decade.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Greece would be better off if it had decided to exit the euro between 2011 and 2015.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C: If Greece had defaulted on (or restructured) its private debt in 2010, while also staying within the euro, that combination would have been better for Greece than either exiting the euro or proceeding as it has actually done.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Bitcoins are more similar to gold than they are to currency.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Bitcoins are more similar to gold than they are to Dutch tulips in the 1630s.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
The US spends roughly 17% of GDP on healthcare, according to the OECD; most European countries spend less than 12% of GDP.
Higher quality-adjusted US healthcare prices contribute relatively more to the extra US spending than does the combination of higher quantity and quality of US care (interpreting quantity and quality to reflect both greater American healthcare needs due to underlying population health and the delivery of more or better healthcare services to Americans).
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
10 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: Prices are obviously key. But even more important is overtreament, due to both carrots (fee per service) and sticks (personal liability)
|
|||
Over the past two years, all else equal, the appeal of the US as a destination for immigrants has changed in ways that will likely decrease innovation in the US economy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A:Holding other policies fixed, the average European would be better off if every European country taxed corporate profits at a rate of 20% (based as closely as possible on a common definition of profits).
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
Comment: Base harmonization is key. Current chaos is inefficient (encourages tax arbitrage) and unfair (profit shifting leads to absurdly low rates)
|
|||
Question B: If other policies were held fixed and every European country taxed corporate profits at a common rate of 20%, then reducing that common rate substantially below 20% would make the average European better off.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
6 |
Strongly Disagree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question A: All else equal, if corporations throughout Europe set quotas for a minimum number of women board members, the shareholder value of European companies would increase.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
5 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: Positive: breaking open old boys network, fairer promotions, visibility of mentors. Negative: choice set is more restricted
|
|||
Question B: Taking into account the likely effects on investments in human capital by men and women, setting quotas throughout Europe for a minimum number of women board members would generate substantial net benefits for Europeans.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
6 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
Comment: Increased diversity eads to more equality of opportunity in society and better decisions (taking better into account all preferences)
|
|||
Question A: Subsidizing renewable energy sources is better than taxing fossil fuels, assuming the subsidy or tax would be set at levels that would reduce carbon emissions by an equivalent amount.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Germany’s solar-energy subsidies to date have produced net social benefits for Germany.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C: Solar-energy subsidies to date in Germany and other countries have produced net social benefits for the world.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Insights from psychology about individual behavior – examples of which include limited rationality, low self-control, or a taste for fairness – predict several important types of observed market outcomes that fully-rational economic models do not.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
8 |
|
|
|
|||
The influx of refugees into Germany beginning in the summer of 2015 will generate net economic benefits for German citizens over the succeeding decade.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Holding labor market institutions and job training fixed, rising use of robots and artificial intelligence is likely to increase substantially the number of workers in advanced countries who are unemployed for long periods.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Rising use of robots and artificial intelligence in advanced countries is likely to create benefits large enough that they could be used to compensate those workers who are substantially negatively affected for their lost wages.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Consumers will be better off, on balance, if European cities treat firms that provide ride-sharing platforms (such as Uber) as substantively different from taxi firms, and thus not necessarily warranting the same regulation.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Assuming that taxi and ride-sharing companies were treated as substantively similar — including requirements that they operate on an equal footing regarding safety, insurance and taxation — letting ride-sharing services compete without restrictions on prices or routes would raise consumer welfare.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C: Regardless of how ride-sharing services are treated, existing regulations for traditional taxi firms in many European cities harm consumers by limiting competition.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Revising France’s labor market policies — by reducing employment protection, decentralizing labor negotiations to the firm level, and making training programs more accessible and responsive to labor demands — would, all else equal, increase productivity in France’s economy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: My own research (with Van Reenen and Lelarge) shows size dependent labour regulations make it hard for productive firms to grow
-see background information here |
|||
Question B: Reducing employment protection would reduce the equilibrium unemployment rate in France.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
9 |
Agree |
7 |
Question A: The ECB's asset purchases over the past two years have reduced the threat of deflation in the euro area as a whole.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: If the economic outlook in the euro area becomes less favorable, then increasing the ECB's asset purchase program (in size or duration) would substantially increase the euro area's economic growth over the following five years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
In general, absent any inside information, an equity investor can expect to do better by holding a well-diversified, low-fee, passive index fund than by holding a few stocks.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
10 |
Strongly Agree |
9 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Without changes in policy, a rising share of people who are over age 65 will exert a substantial downward influence on per capita real GDP in western European countries.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: In European countries where the share of those over 65 is rising, there are net social benefits to adjusting retirement ages for state-financed (including pay-as-you-go) pension systems upwards, so that revised retirement ages better reflect longer life expectancies.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
No Opinion |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: All else equal, there are substantial advantages to having much of Europe’s human capital and infrastructure for international financial activity clustered in a single city, as they are at present in London.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
5 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: There exist some agglomeration economies. It is unclear however how substantial they are, with ICT playing a growing role in Finance
|
|||
Question B: All else equal, Britain’s rules on hiring, firing and working hours are significantly more conducive to financial activity than those in other large European countries.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: The legal environment, safe, fast and low cost in the UK, is key. This goes beyond labor costs into Secutities and IPO cost etc.
|
|||
Question A: Setting the EU rules aside, and assuming it would take 2.5% of Italy’s GDP to recapitalize its banks, the Italian government would improve financial stability in Europe if it injected this amount of public funds into its banks.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
4 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: A bailout is probably good in short term for Financial Stability. But undermines new Euro BRRD framework and opens door to populists.
-see background information here -see background information here |
|||
Question B: If Italy were to inject public funds into its banks without imposing losses on at least some claimants, an important cost would be the effect on future incentives (economic or political) in Europe.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
6 |
Agree |
8 |
|
Comment: At the very least it would introduce confusion among investors as the BRRD framework requires 8% bail in.
|
|||
Question A: Because of the Brexit vote's outcome, the UK's real per-capita income level is likely to be lower a decade from now than it would have been otherwise.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
8 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Because of the Brexit vote's outcome, the rest of the EU's real per-capita income level is likely to be lower a decade from now than it would have been otherwise.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
In general, using more congestion charges in crowded transportation networks — such as higher tolls during peak travel times in cities, and peak fees for airplane takeoff and landing slots — and using the proceeds to lower other taxes would make citizens on average better off.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Strongly Agree |
8 |
|
|
|
|||
On the whole, the shift from state to private ownership of many industrial assets in central and eastern European countries after communism has increased productivity in those countries.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Strongly Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Freer movement of goods and services across borders within Europe has made the average western European citizen better off since the 1980s.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Strongly Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Freer movement of goods and services across borders within Europe has made many low-skilled western European citizens worse off since the 1980s.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
9 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Giving tax incentives to specific firms to locate operations in a country typically generates domestic benefits that outweigh the costs to the country providing the incentives.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Europe as a whole benefits when European cities or countries compete with each other by giving tax incentives to firms to locate operations in their jurisdictions.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Freer movement of people to live and work across borders within Europe has made the average western European citizen better off since the 1980s.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Freer movement of people to live and work across borders within Europe has made many low-skilled western European citizens worse off since the 1980s.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
6 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
|
|||