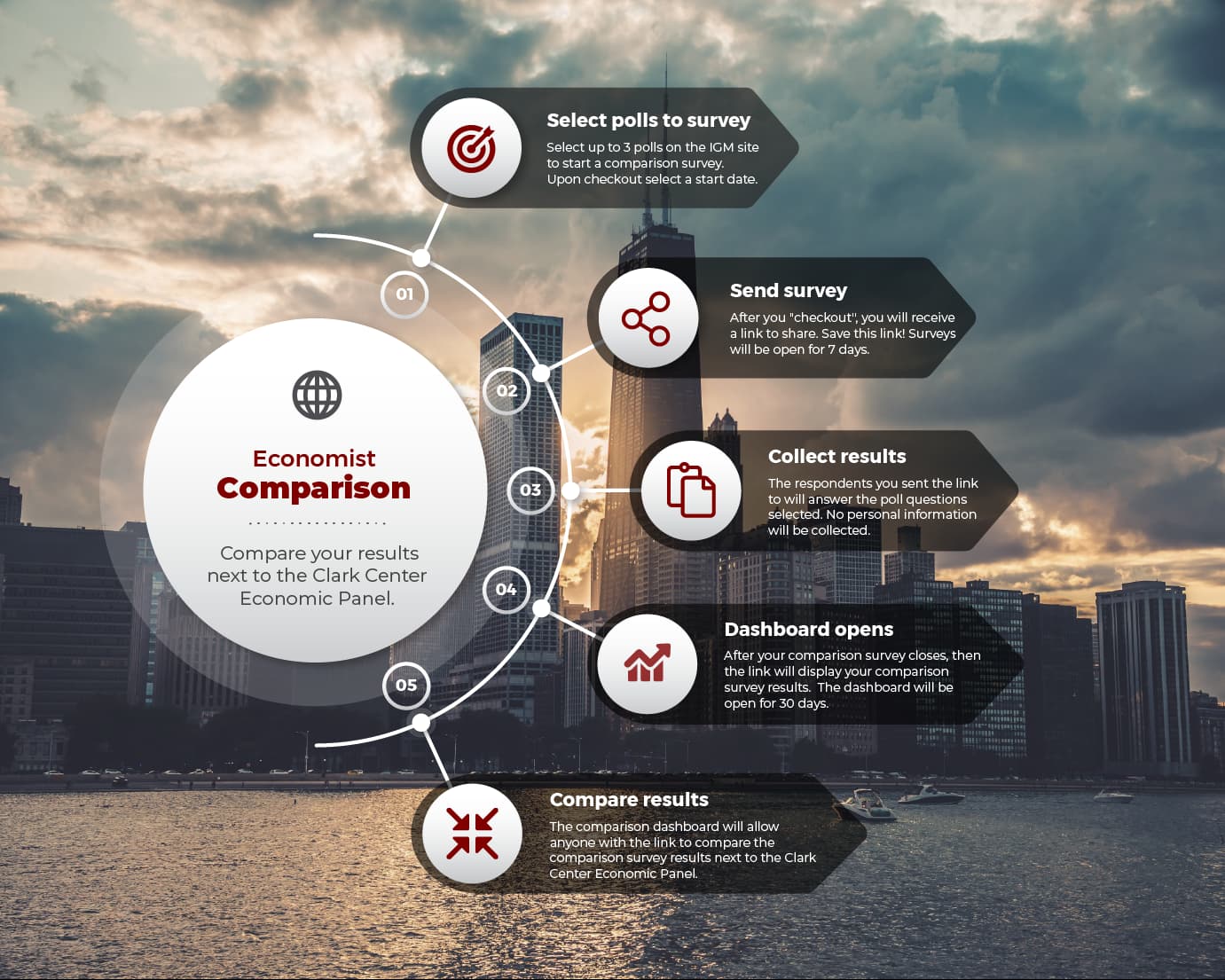
About
- Professor of International Economics, The Graduate Institute, Geneva
- Distinguished Fellow in residence, INSEAD Asian Campus, Singapore
- Member of the German Council of Economic Experts, Wiesbaden (2004–12)
- CEPR Research Fellow (since 2003)
Voting History
Question A: Right now, the central focus of fiscal policy should be on temporary measures to provide protection and promote rapid economic recovery rather than trying to advance other objectives, such as reducing debt, tackling climate change or addressing inequality.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
8 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Cutting taxes on firms (or delaying tax collection) will allow more of them to survive and be more effective than public spending for triggering a rapid economic recovery.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C: European recovery fund disbursements to crisis-hit countries should be primarily in the form of grants rather than loans.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question D: European recovery fund disbursements to crisis-hit countries should not be made on condition of commitments to reform by recipients.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
8 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Given the social and regulatory pressures to keep prices down for drugs and vaccines to treat Covid-19, the financial incentives for pharmaceutical companies to invest in such products are below the value of the investment to society.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Government commitments to pay developers and manufacturers above average costs for an effective vaccine or drug treatments for Covid-19 would accelerate production.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C: Given the positive externalities from vaccination, an effective Covid-19 vaccine should have priority in public healthcare funding even in countries where other diseases cause more death and disability.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Political conflict plays a key role in shaping economic decisions, policies and outcomes.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
8 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Most European countries have larger social welfare systems than the United States in part because the latter is more heterogeneous by race and ethnicity.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Clearing the market for surgical face masks using prices is detrimental to the public good.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Laws to prevent high prices for essential goods in short supply in a crisis would raise social welfare.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C: Governments should buy essential medical supplies at what would have been the market price and redistribute according to need rather than ability to pay.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Economic damage from the virus and lockdowns will ultimately fall disproportionately hard on low- and middle-income countries.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: A temporary standstill on sovereign debt payments by low- and middle-income countries to all official and private creditors to give those countries space to cover the immediate costs of the crisis would benefit advanced economies.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C: Export restrictions on food and medical supplies, and other protectionist measures, are likely to cost lives and slow economic recovery in all countries.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Government support to private firms in the form of debt (either directly or with the help of public guarantees) is desirable, but risks leaving them with too much leverage to invest and grow in the future.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
9 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Providing funds to viable businesses in the form of equity injections is a vital complement to debt support.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
5 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
Comment: Equity is only one form of dealing with the problem
|
|||
Question C: With the EU ban on state aid suspended, government capital injections should be provided via a newly created pan-European equity fund, rather than be left to national governments acting independently.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A:Even with the support policies implemented by European governments in response to the crisis, low-income workers will suffer a relatively bigger hit to their incomes than those further up the distribution.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: With schools across Europe closed in the lockdown, existing gaps in access to quality education between high- and low-income households will be exacerbated.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
8 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C: Combating the effects of the pandemic on inequality should be a priority for policy interventions.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Severe lockdowns – including closing non-essential businesses and strict limitations on people’s movement – are likely to be better for the economy in the medium term than less aggressive measures.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Agree |
8 |
|
Comment: because it may allow faster reopen.
|
|||
Question B: While national governments have responded to the crisis with substantial economic policy measures, a joint euro area fiscal response is still highly desirable.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
10 |
Strongly Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question C: Given the willingness of the European Central Bank to buy sovereign bonds, including Italian bonds, without limits, there is no need for ‘coronabonds’.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
5 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
Comment: Europe will need several fiscal instruments to tackle different issues of mitigating this crisis, rebooting and opening borders again.
|
|||
Question A: Even if the mortality of COVID-19 proves to be limited (similar to the number of flu deaths in a regular season), it is likely to cause a major recession.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: The economic effects of COVID-19 coming from reduced spending will be larger than those coming from disruptions to supply chains and illness-related workforce reductions.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C: The economic policy institutions of the Eurozone are well equipped to ameliorate the potential economic damage from COVID-19.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Germany's current account surplus is undesirable even from a purely German viewpoint: the country would be better off if, for example, it ran a smaller primary surplus, in turn leading to a smaller current account surplus.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: The Eurozone would be in better shape if fiscal policy were more expansionary, which would allow monetary policy to be slightly less so.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C: If there is a recession in the Eurozone, it will be essential to have a coordinated fiscal expansion.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
8 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: The European Union goal of reaching net zero emissions of greenhouse gases by 2050 will be a major drag on economic growth.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Disagree |
8 |
Disagree |
5 |
|
Comment: All depends on how it is implemented. With a credible pathway it could boost public and private investment while reallocating capital.
|
|||
Question B: Carbon taxes are a better way to implement climate policy than cap-and-trade.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
9 |
Agree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question C: A carbon border tax targeting imports from non-EU countries with less strict climate policies is likely to harm developing economies.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
7 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Following the UK election result, the certainty that the country is going to leave the European Union will provide a substantial short-term boost to the UK economy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
8 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Given that the transition period currently expires at the end of 2020, there is still a considerable risk that the UK will leave the European Union without a trade agreement.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question C: Leaving the European Union without a trade agreement would have a large negative impact on the UK economy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Under current policies on climate change, the associated physical risks (such as those arising from total seasonal rainfall and sea level changes, and increased frequency, severity, and correlation of extreme weather events) will be at most a very small factor in monetary policy decisions over the next decade.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
5 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question B: The physical risks associated with climate change under current policies are likely to threaten financial stability over the next decade.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
9 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Europeans would benefit more from an extra €1 billion of public R&D spent through existing (public) channels than from an extra €1 billion of private R&D spent through existing (private) channels, all else equal.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Europeans would benefit more from an extra €1 billion of public medical research spent through existing (public) channels than from an extra €1 billion of private medical research spent through existing (private) channels, all else equal.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Randomized control trials are a valuable tool for answering some long unsettled questions in development economics research.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
5 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Randomized control trials are a valuable tool for making significant progress in poverty reduction.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
5 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Having companies run to maximize shareholder value creates significant negative externalities for workers and communities.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Appropriately managed corporations could create significantly greater value than they currently do for a range of stakeholders – including workers, suppliers, customers and community members – with small impacts on shareholder value.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C:Effective mechanisms for boards of directors to ensure that CEOs act in ways that balance the interests of all stakeholders would be straightforward to introduce.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A:Rising inequality is straining the health of liberal democracy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: But income inequality is only one of the issues and in many countries not the main one. In many regional inequality is more important.
|
|||
Question B: Enacting more redistributive expenditures and policies would be likely to limit the rise of populism in Europe.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question C: European governments should allocate more resources to policies that would be likely to limit the rise of populism in Europe, even if it means higher public debt or lower public spending in other areas.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
9 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A:At this point, there is little that the European Central Bank can do to increase or maintain output in the Eurozone.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
6 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
Comment: Not much much with the existing toolkit
|
|||
Question B: When the economy is operating below its potential, larger fiscal deficits are likely to increase demand and output.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
9 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: The question is how much.
|
|||
Question C: When the economy is operating below its potential and monetary policy is at the effective lower bound, fiscal policy should prioritize increasing output over decreasing public debt.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
7 |
Uncertain |
7 |
|
Comment: Depends on the debt level
|
|||
Question A:Selecting candidates for membership of the ECB Executive Board based primarily on nationality ahead of competence is likely to have a negative effect on the quality of monetary policy in the Eurozone.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
8 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Although the central bank can never be an entirely technocratic institution, the selection process for the ECB President and members of the Executive Board is significantly worsened by intergovernmental trade-offs involving appointments to other European institutions.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
8 |
|
|
|
|||
On bids for infrastructure projects, the average European would be better off if Europe’s governments favored European firms over Chinese firms (or firms from any other country with non-profit-related geopolitical strategies) — even if it means sometimes choosing a higher-cost bidder.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Breaking the “doom loop” — a negative spiral that can result when banks hold sovereign bonds and governments bail out banks — would increase the stability of European economies in the event of another financial crisis.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
10 |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Regulators should try to break the doom loop by assigning positive risk weights — in calculating banks’ capital requirements — to banks’ holdings of domestic and other Eurozone sovereign bonds.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
10 |
Agree |
8 |
|
Comment: Risk weights not the best instrument for diversification. Concentration rules are an alternative and safe assets a necessary complement.
-see background information here |
|||
Question C: Breaking the doom loop would impose substantial costs on powerful political constituencies.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Uncertain |
8 |
|
Comment: Depends on how it is done and on the package
|
|||
Residents of big European cities would be better off, on balance, if governments did more to counter gentrification, for example by using rent and other housing subsidies, public housing investments, zoning regulations, or similar policies.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: A common European deposit insurance scheme, once fully implemented, would increase the stability of European economies in the event of another financial crisis.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
10 |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question B: A common European deposit insurance scheme, once fully implemented, would increase the likelihood of another financial crisis in Europe.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Disagree |
10 |
Strongly Disagree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Overall, public spending on the arts in Europe creates benefits that exceed the deadweight loss caused by taxation to fund it.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Additional public spending on the arts in Europe would create incremental benefits that exceed the deadweight loss caused by taxation to fund it.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: The average European is better off if Europe’s competition authorities let firms merge into European champions in their sectors, even it weakens competition.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Disagree |
7 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: If China and other countries use policies that create giant international firms, then the average European is better off if Europe's competition authorities let firms merge into European champions in their sectors, even it weakens competition.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
6 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Letting publicly traded European firms report earnings annually rather than quarterly would lead their executives to place more weight on long-term issues in their investments and other decisions.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: A switch from quarterly to annual earnings reports would, on net, benefit shareholders of European firms.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: To the extent that public corporations pursue social and environmental initiatives, they tend to achieve higher risk-adjusted (private) returns than otherwise similar corporations that pursue such initiatives less.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: To the extent that Norway’s global government pension fund makes investments for social and environmental objectives — apart from investments that would bring the highest expected risk-adjusted returns — it improves the welfare of Norwegians.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: The fiscal rules of the European Union should give more flexibility to member countries.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
10 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: Mostly it is about making the rules less pro-cyclical and less policially divisive (see CEPR Policy Insight 91)
|
|||
Question B: The Italian budget for 2019 that the European Commission rejected in October would have increased Italy’s risk of fiscal insolvency substantially.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: It’s not mainly about debt sustainably but about the risk of a run on the debt.
|
|||
Question C: If France runs a 2019 budget deficit of around 3.4% of GDP, as announced by President Macron’s government, France’s risk of fiscal insolvency will increase substantially.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
1 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
Comment: Not solvency but the ability of the French government to push reform of the Euro area is immediately at risk.
|
|||
Question A: Capping the number of ride-sharing drivers as is being discussed in New York City, Chicago and London will make the average resident in that city worse off.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B:To achieve a given level of congestion, it would be better to use taxes for driving that vary based on the level of congestion, rather than limiting the number of ride-sharing vehicles.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
8 |
|
|
|
|||
People who migrated to Europe between 2015 and 2018 are likely — over the next two decades — to contribute more in taxes paid than they receive in benefits and public services.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Ideas are nonrival, so increasing returns to scale is an essential feature of technological change in a market economy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Voters overestimate the effect that current governments have on their economies’ concurrent economic performance.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Over the next decade, autonomous cars will raise average welfare in the EU by at least as much as smartphones have over the past decade.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
7 |
Disagree |
5 |
|
|
|||
Britain’s Labour party recently proposed giving the Bank of England a target of 3% annual labor productivity growth. Consider the following statement:Central banks cannot significantly increase productivity growth over a ten year horizon, except perhaps by promoting macroeconomic stability.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
9 |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question A: The European Commission has proposed new rules to ensure that “digital business activities are taxed in a fair and growth-friendly way in the EU”. Consider two statements regarding this proposal:An EU-wide 3% tax on revenue from digital activities would, on balance, be a good idea.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B:If the EU decides to tax digital service providers, it would be better — given the difficulties of measuring and verifying digital activity — to tax them on the revenue, rather than the profits, that they generate locally.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
The European Union often uses its antitrust powers to protect EU-based firms from international competition, rather than to promote greater competition in European markets.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Strongly Disagree |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Trade with China makes most Europeans better off because, among other advantages, they can buy goods that are made or assembled more cheaply in China.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
8 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Some Europeans who work in the production of competing goods, such as clothing and furniture, are made worse off by trade with China.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C: If the EU followed the new US steel tariffs by imposing similar EU tariffs on steel from China, it would improve Europeans’ welfare.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Strongly Disagree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Assuming it exits its third bailout program this summer without an immediate restructuring or other debt relief, Greece is unlikely to default on its sovereign debt in the coming decade.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: Gross financing needs only increase later, in the short run they ar low due to highly concessional conditions on European loans.
|
|||
Question B: Greece would be better off if it had decided to exit the euro between 2011 and 2015.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Disagree |
9 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question C: If Greece had defaulted on (or restructured) its private debt in 2010, while also staying within the euro, that combination would have been better for Greece than either exiting the euro or proceeding as it has actually done.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
1 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Bitcoins are more similar to gold than they are to currency.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
9 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
Comment: The bitcoin supply is asymptotically fixed , as opposed to fiat money.
|
|||
Question B: Bitcoins are more similar to gold than they are to Dutch tulips in the 1630s.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Disagree |
8 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
Comment: Fantasy plays a large part in the pricing of bitcoin.
|
|||
The US spends roughly 17% of GDP on healthcare, according to the OECD; most European countries spend less than 12% of GDP.
Higher quality-adjusted US healthcare prices contribute relatively more to the extra US spending than does the combination of higher quantity and quality of US care (interpreting quantity and quality to reflect both greater American healthcare needs due to underlying population health and the delivery of more or better healthcare services to Americans).
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Over the past two years, all else equal, the appeal of the US as a destination for immigrants has changed in ways that will likely decrease innovation in the US economy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
Comment: Many students and researchers are no longer interested in going to the US
|
|||
Question A:Holding other policies fixed, the average European would be better off if every European country taxed corporate profits at a rate of 20% (based as closely as possible on a common definition of profits).
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: If other policies were held fixed and every European country taxed corporate profits at a common rate of 20%, then reducing that common rate substantially below 20% would make the average European better off.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Strongly Disagree |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: All else equal, if corporations throughout Europe set quotas for a minimum number of women board members, the shareholder value of European companies would increase.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
6 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Taking into account the likely effects on investments in human capital by men and women, setting quotas throughout Europe for a minimum number of women board members would generate substantial net benefits for Europeans.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Subsidizing renewable energy sources is better than taxing fossil fuels, assuming the subsidy or tax would be set at levels that would reduce carbon emissions by an equivalent amount.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Germany’s solar-energy subsidies to date have produced net social benefits for Germany.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Disagree |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C: Solar-energy subsidies to date in Germany and other countries have produced net social benefits for the world.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
5 |
|
|
|
|||
Insights from psychology about individual behavior – examples of which include limited rationality, low self-control, or a taste for fairness – predict several important types of observed market outcomes that fully-rational economic models do not.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
8 |
|
|
|
|||
The influx of refugees into Germany beginning in the summer of 2015 will generate net economic benefits for German citizens over the succeeding decade.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
9 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
Comment: Most refugees lack the skills to be quickly integrated into the German labor market. EducatIon and integration policies will be key
|
|||
Question A: Holding labor market institutions and job training fixed, rising use of robots and artificial intelligence is likely to increase substantially the number of workers in advanced countries who are unemployed for long periods.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
10 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Rising use of robots and artificial intelligence in advanced countries is likely to create benefits large enough that they could be used to compensate those workers who are substantially negatively affected for their lost wages.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
5 |
Agree |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Consumers will be better off, on balance, if European cities treat firms that provide ride-sharing platforms (such as Uber) as substantively different from taxi firms, and thus not necessarily warranting the same regulation.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|
|||
Question B: Assuming that taxi and ride-sharing companies were treated as substantively similar — including requirements that they operate on an equal footing regarding safety, insurance and taxation — letting ride-sharing services compete without restrictions on prices or routes would raise consumer welfare.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question C: Regardless of how ride-sharing services are treated, existing regulations for traditional taxi firms in many European cities harm consumers by limiting competition.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | Agree |
7 |
|
|
|
|||
Question A: Revising France’s labor market policies — by reducing employment protection, decentralizing labor negotiations to the firm level, and making training programs more accessible and responsive to labor demands — would, all else equal, increase productivity in France’s economy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
5 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Reducing employment protection would reduce the equilibrium unemployment rate in France.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
5 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A: The ECB's asset purchases over the past two years have reduced the threat of deflation in the euro area as a whole.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: If the economic outlook in the euro area becomes less favorable, then increasing the ECB's asset purchase program (in size or duration) would substantially increase the euro area's economic growth over the following five years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Uncertain |
5 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|||
In general, absent any inside information, an equity investor can expect to do better by holding a well-diversified, low-fee, passive index fund than by holding a few stocks.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
5 |
Strongly Agree |
9 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Without changes in policy, a rising share of people who are over age 65 will exert a substantial downward influence on per capita real GDP in western European countries.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
9 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: In European countries where the share of those over 65 is rising, there are net social benefits to adjusting retirement ages for state-financed (including pay-as-you-go) pension systems upwards, so that revised retirement ages better reflect longer life expectancies.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
10 |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question A: All else equal, there are substantial advantages to having much of Europe’s human capital and infrastructure for international financial activity clustered in a single city, as they are at present in London.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Disagree |
9 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: All else equal, Britain’s rules on hiring, firing and working hours are significantly more conducive to financial activity than those in other large European countries.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
6 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Setting the EU rules aside, and assuming it would take 2.5% of Italy’s GDP to recapitalize its banks, the Italian government would improve financial stability in Europe if it injected this amount of public funds into its banks.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
7 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question B: If Italy were to inject public funds into its banks without imposing losses on at least some claimants, an important cost would be the effect on future incentives (economic or political) in Europe.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
9 |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Because of the Brexit vote's outcome, the UK's real per-capita income level is likely to be lower a decade from now than it would have been otherwise.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Because of the Brexit vote's outcome, the rest of the EU's real per-capita income level is likely to be lower a decade from now than it would have been otherwise.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
8 |
Agree |
7 |
|
|
|||
In general, using more congestion charges in crowded transportation networks — such as higher tolls during peak travel times in cities, and peak fees for airplane takeoff and landing slots — and using the proceeds to lower other taxes would make citizens on average better off.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Strongly Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
On the whole, the shift from state to private ownership of many industrial assets in central and eastern European countries after communism has increased productivity in those countries.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Agree |
6 |
Strongly Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Freer movement of goods and services across borders within Europe has made the average western European citizen better off since the 1980s.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
1 |
Strongly Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Freer movement of goods and services across borders within Europe has made many low-skilled western European citizens worse off since the 1980s.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
7 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Giving tax incentives to specific firms to locate operations in a country typically generates domestic benefits that outweigh the costs to the country providing the incentives.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
6 |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Europe as a whole benefits when European cities or countries compete with each other by giving tax incentives to firms to locate operations in their jurisdictions.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Disagree |
6 |
Disagree |
7 |
|
|
|||
Question A: Freer movement of people to live and work across borders within Europe has made the average western European citizen better off since the 1980s.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Agree |
10 |
Agree |
8 |
|
|
|||
Question B: Freer movement of people to live and work across borders within Europe has made many low-skilled western European citizens worse off since the 1980s.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Strongly Disagree |
9 |
Disagree |
6 |
|
|
|||