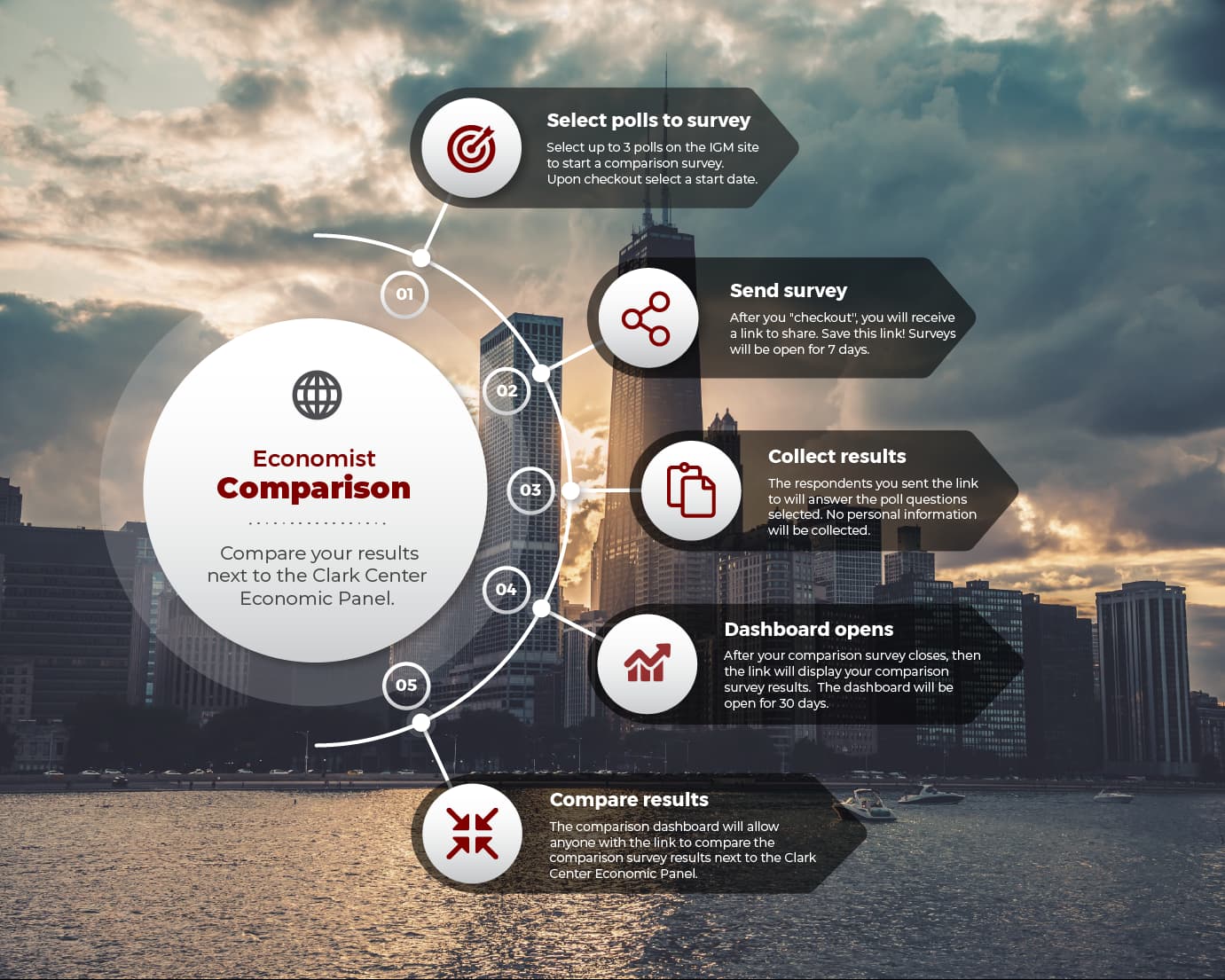
The Clark Center for Global Markets explores economists’ views on vital policy issues via our US and European Economic Experts Panels. We regularly poll over 80 economists on a range of timely and relevant topics. Panelists not only have the opportunity to respond to a poll’s statements, but an opportunity to comment and provide additional resources, if they wish. The Clark Center then shares the results with the public in a straightforward and concise format.
Please note that from September 2022, the language in our polls will use just two modifiers to refer to the size of an effect:
- ‘Substantial’: when an effect is large enough that it would make a difference that matters for the behavior involved.
- ‘Measurable’: when the direction of the effect is clear, but perhaps experts would differ as to whether it is substantial.