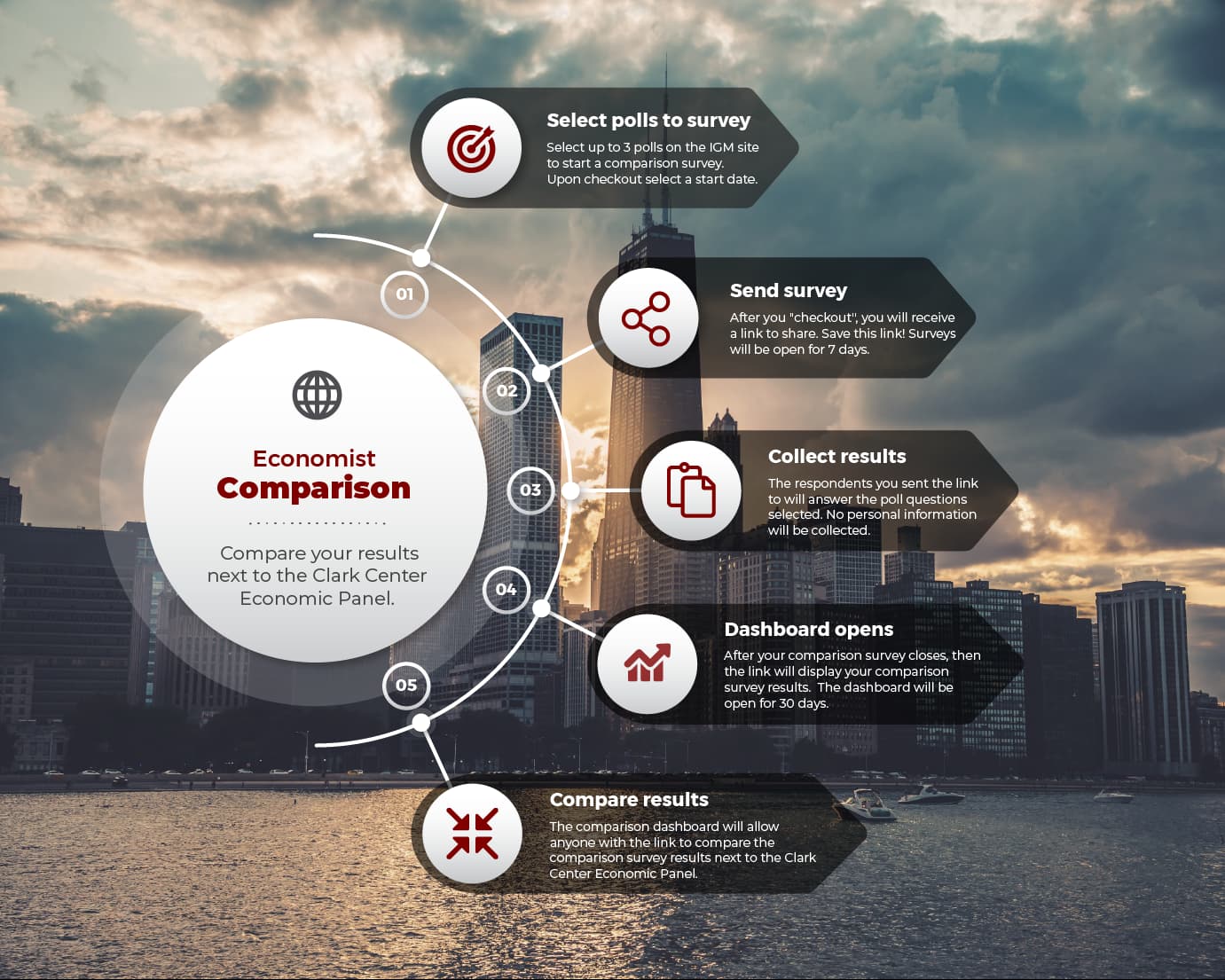
About
- George C. Tiao Distinguished Service Professor of Economics
- Editor Journal of Political Economy (2018—2022)
- National Academy of Sciences Panel on Reengineering the Census Bureau’s Annual Economic Surveys (2015—2018)
Voting History
Question A: The institutions of society - such as constitutions, laws, judiciaries, and property rights - substantially shape economic decisions, policies, and outcomes.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
Question B: On average and over the long term, democracies deliver substantially better economic growth than other forms of government.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Comment: Seems that a summary of the best estimates in the literature indicate a positive but modest causal effect, but this stuff is inherently hard to measure well
|
|||
Question C: Countries where democracy and the rule of law are weakened are likely to experience measurable damage to their economic performance.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
Question A: The Democrats and Republicans have floated the idea of a US sovereign wealth fund. For background, see here and here.
Establishing a domestic sovereign wealth fund to invest in infrastructure, emerging technologies, and/or strategic sectors would bring substantial benefits to the US economy over a ten-year horizon.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
Question B: The typical advanced economy could substantially boost growth by establishing a sovereign wealth fund to invest in infrastructure, emerging technologies, and/or strategic sectors.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
Question C: For a typical advanced economy, establishing a sovereign wealth fund would be substantially better for citizens relative to paying down the debt as a use for excess revenue.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
Question A: Capping annual rent increases by corporate landlords at 5%, as proposed by President Biden, would make middle-income Americans substantially better off over the next ten years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Comment: Dear Lord please don't.
|
|||
Question B: Capping annual rent increases at 5%, as proposed by President Biden, would substantially reduce the amount of available apartments for rent over the next ten years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Comment: If a return cap on any asset might bind, you will reduce investment in that asset, all else equal.
|
|||
Question C: Capping annual rent increases at 5%, as proposed by President Biden, would substantially reduce US income inequality over the next ten years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
Question A: All else equal, making permanent the 2017 tax cuts that were set to expire at the end of 2025 would substantially increase federal deficits and the federal debt over the coming decade.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Comment: "All else equal" doing some work here, as in isolation continuing the tax cut will increase deficits relative to expiration; it has not come near to paying for itself
-see background information here |
|||
Question B: All else equal, making permanent the 2017 tax cuts that were set to expire at the end of 2025 would measurably increase the rate of US economic growth over the coming decade.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Comment: This is a tough one. The evidence indicates capital accumulation benefits of 2017 TCJA, but we are entering a fiscal situation where continued large deficits might hamper long-run growth.
-see background information here |
|||
Question C: In the US, given Congressional budget scoring rules, temporary tax cuts generate sufficient pressure for extension as to be effectively permanent.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
Question A: The lower willingness of private firms to go public, combined with the increased number of publicly traded firms being taken private over the last 25 years, is measurably net negative for economic growth.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Comment: I'm not clear on this one at all. Maybe startups' strategy shift from IPO to acquisition is somewhat harmful, but beyond that I just don't know.
|
|||
Question B: All else equal, reducing regulatory barriers (including reporting requirements such as Sarbanes Oxley 404) to public listing would substantially increase the share of publicly traded firms in the economy.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Comment: If you reduce the cost of doing something that is beneficial to someone, they will do more of it.
|
|||
Question C: The lack of transparency about unlisted private firms' financial performance substantially hinders the efficiency of the allocation of capital.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Comment: I would defer strongly to my accounting colleagues here.
|
|||
Question A: Antitrust investigations of the dominant firms in artificial intelligence are likely to lead to substantially lower prices of AI products and services for businesses and consumers.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | |||
|
|
|||
Question B: Antitrust investigations of the dominant firms in artificial intelligence are likely to promote greater competition and innovation in AI.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | |||
|
|
|||
Question C: Potential harms from artificial intelligence are better assessed by market deployment rather than seeking to slow the pace of AI research and implementation.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | |||
|
|
|||
Question A: The proposed US tariffs on Chinese EVs would lead to measurably higher employment in the US automotive industry over the next five years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Comment: US employment effect depends on many factors and margins of substitution; e.g., do Chinese manufacturers move production and to where, can U.S. producers ramp up EV and how does this cannibalize their ICE sales
|
|||
Question B: The proposed US tariffs on Chinese EVs would lead to measurably higher prices of EVs in the US.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
Question C: The proposed US tariffs on Chinese EVs would measurably slow the adoption of green technology by consumers.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
Reclassifying marijuana as a Schedule III drug would lead to measurably higher social welfare.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Comment: Schedule I for marijuana is a decades-old mistake that created massive enforcement costs (direct and spillover). Moving away from it helps. Further moves in that direction may be optimal.
|
|||
Question A: Tripling existing import taxes on Chinese steel and aluminum products would lead to measurably higher employment in the US steel industry over the next five years.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Comment: Lots of substitution margins around Chinese-produced steel and aluminum, of which shift to domestic employment is only one.
|
|||
Question B: Tripling the tariffs would lead to measurably higher steel and aluminum prices for American producers and measurably higher finished-good prices for American consumers.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Comment: Size depends on available substitution margins, but hard to imagine how it would ever reduce finished-goods prices.
|
|||
Question C: The gains for the American economy from tripling the tariffs would measurably outweigh the losses.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Comment: I believe there are agglomerative forces in manufacturing, but these sectors don't seem the place for large ones.
|
|||
Universities that abandon temporary pandemic test-optional policies and return to requiring standardized test scores for admissions will create measurably enhanced opportunities for potentially high-achieving students from low-income backgrounds.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Comment: In absence of standardized scores, schools could switch and were switching to even more (income-correlated) manipulable criteria. I'm a little surprised anyone who ever went to school in a mixed income environment expected any other outcome.
|
|||
Question A: The FTC is opposed to Kroger’s proposed acquisition of Albertsons. Critics argue that with sufficient divestitures, the deal would be consistent with past FTC policies.
Kroger’s proposed acquisition of Albertsons would lead to substantially higher grocery prices and/or lower product quality/services for customers of the two companies in locations where both are present.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | |||
|
|
|||
Question B: Kroger’s proposed acquisition of Albertsons would have a substantially negative effect on workers at the two companies in locations where both are present.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Answer | |||
|
|
|||
Question A: Allowing Medicare to negotiate prices with pharmaceutical companies will lead to a substantial reduction in the costs of prescription drugs for US retirees.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Comment: In the short run, certainly. Everyone raises future innovation effects, and I understand the argument, but I'm not sure why the government paying P>>>MC on the margin is the way to subsidize research. Drug-by-drug, I think it makes sense for gov't to bargain like any other buyer.
|
|||
Question B: Allowing imports of medicines from Canada will lead to a substantial reduction in the costs of prescription drugs for US consumers without compromising safety.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Comment: I think the equilibrium is harder to predict for re-importation than Medicare/Medicaid bargaining. But I think some price drops are more likely than not.
|
|||
Question A: A tolling program for New York City is out for public consultation with proposed charges on vehicles entering the central business district of Manhattan summarized here: https://new.mta.info/document/129191
The proposed tolls on vehicles entering the central business district of Manhattan are likely to lead to a substantial reduction in traffic congestion in the targeted area.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Comment: London saw a decrease in traffic for a few years but in the long run it seems to have come back. (Though of course it is hard to know the counterfactual; traffic could well be even worse now if not for the congestion charge.)
|
|||
Question B: The proposed tolls on vehicles entering Manhattan are likely to lead to a substantial increase in traffic congestion just outside the central business district, above 60th Street, in the outer boroughs and New Jersey.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Comment: We usually see some substitution to spatial pricing, though again it is difficult to know how much to expect in this case.
|
|||
Question A: The economic and financial sanctions against Russia are substantially limiting its ability to wage war on Ukraine.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Comment: Russian gov't revenues have been affected by oil price cap, and sanctions have made it harder to obtain certain parts important for military industrial production. Though it seems they are increasingly finding ways around the latter.
|
|||
Question B: In the absence of continuing flows of Western economic aid, Ukraine's wartime economy will be substantially compromised.
| Vote | Confidence | Median Survey Vote | Median Survey Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||